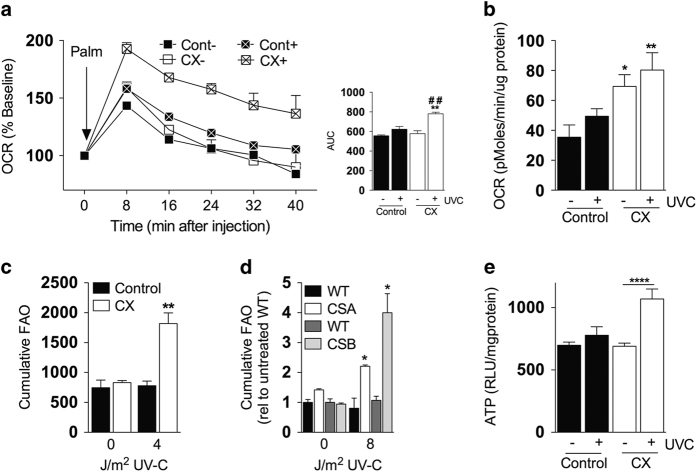
Figure 3.
Increased fatty acid oxidation (FAO) is a cell-autonomous, adaptive response triggered by genotoxic stress in CX cells. (a) Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) over time after the injection of 200 μ mol/l bovine serum albumin (BSA)-conjugated palmitate in the indicated genotypes (n=3 independent mouse dermal fibroblasts (MDF) lines/genotype) 24 h post 4 J/m2 ultraviolet (UV)-C or mock treatment (+ or −, respectively) with AUC analysis at right; Student’s t-test between genotypes within UV treatment group**; Student’s t-test within genotype between ±UV treatment##. (b) OCR of MDFs (three lines/genotype) 24 h after 4 J/m2 UV-C or mock treatment; one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) between genotypes within treatment group with Dunnett's post-test. (c) Cumulative FAO of tritiated palmitate over a 4 h period, 24 h after treatment of MDFs (n=3 lines/genotype) with indicated dose of UV-C; Student’s t-test between genotypes within UV dose. (d) Primary human CSA and CSB dermal fibroblasts treated as in (c); Student’s t-test between genotypes within UV dose. (e) Steady-state ATP levels of MDFs 24 h after exposure to 0 or 4 J/m2 UV-C; Student’s t-test within genotype between ±UV treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, ##P<0.01.