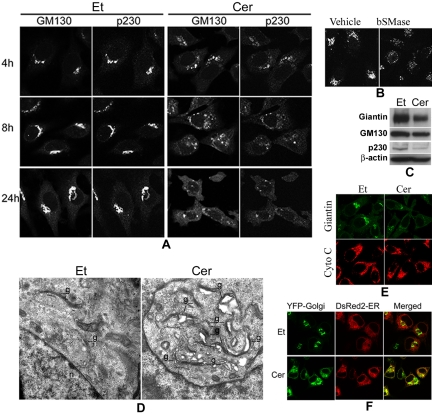
Figure 6.
Treatment with D-e-ceramide causes the fragmentation of the Golgi complex and inhibits protein exit from the ER. (A) HeLa cells treated with D-e-Cer or Et for various time durations were colabeled with antibodies against GM130 and p230-Trans before confocal microscopic analyses. (B) Two hours after treatment with 0.4 U/ml bSMase or the vehicle (glycerol), HeLa cells were stained with the anti-giantin antibody and analyzed by confocal microcopy. (C) Sixteen hours posttreatment with D-e-Cer or Et, expression of giantin, GM130, and p230-Trans was determined by Western blot analysis with their corresponding antibodies. (D) HeLa cells treated with Et or 2.5 μM D-e-Cer for 1 h were fixed and subjected to electronic microscopic analysis. g, Golgi complex; n, nucleus. (E) Note the formation of vacuoles closely associated with the partially ruptured Golgi complex in the D-e-Cer–treated cells. HeLa cells treated with D-e-Cer (2.5 μM) or Et for 4 h before coimmunostaining with antibodies against giantin and cytochrome C (Cyto C), respectively. (F) Twelve hours post-transfection with plasmid pEYFP-Golgi and pDsRed2-ER, HeLa cells were treated with D-e-Cer or vehicle for 6 h. The live cells were imaged under the confocal microscope. This figure is representative of multiple independent experiments.