Figure 5.
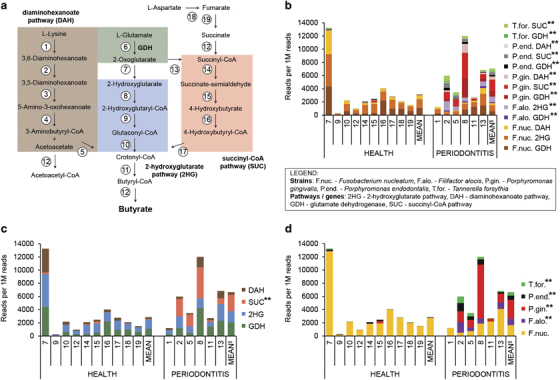
Pathways involved in butyrate production and their expression in health and periodontitis. (a) Scheme of the proposed pathways utilised by oral bacteria to produce butyrate from lysine, glutamate and aspartate: the diaminohexanoate pathway (DAH, highlighted in brown) of lysine degradation consists of the following enzymes (numbers within circles): (1) L-lysine-2,3-aminomutase, (2) L-β-lysine-5,6-aminomutase, (3) 3,5-diaminohexanoate dehydrogenase, (4) 3-keto-5-aminohexanoate cleavage enzyme, (5) 3-aminobutyryl-CoA deaminase. The glutamate dehydrogenase pathway (GDH, highlighted in green) catalyses the reaction number (6). The 2-hydroxyglutarate pathway (2HG, highlighted in blue) of glutamate catabolism consists of following enzymes: (7) 2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase, (8) glutaconate (2-hydroxyglutarate) CoA-transferase, (9) 2-hydroxyglutaryl-CoA dehydratase, (10) glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase, (11) butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, (12) acyl-CoA:acetate CoA/acetoacetate CoA-transferase, (13) 2-oxoglutarate oxidoreductase. The succinyl-CoA pathway (SUC, highlighted in red) of glutamate catabolism consists of the following enzymes: (14) succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase, (15) 4-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase, (16) 4-hydroxybutyrate coenzyme A transferase, (17) 4-hydroxyphenylacetate-3-hydroxylase/4-hydroxybutyryl dehydratase. l-Aspartate can be metabolised to succinate by (18) and (19) that are aspartate aminotransferase and fumarate reductase, respectively. Succinate can enter the succinyl-CoA pathway (SUC). The presented pathways were adapted from refs 60–62. (b) Abundance of reads grouped to the six species and four pathways highlighted in a. The values are plotted on the left and right side for the healthy individuals and those with periodontitis, respectively. Mean values for both the groups are also shown. The legend with the list of abbreviations is located below the figure. (c) Same as b but reads are grouped to pathways only. Colours are in accordance with those used in a. (d) Same as b but reads are grouped to species only. Colours are in accordance with those used in b. **, showed statistically significant (P<0.01) higher abundance in the communities from individuals with periodontitis. The outlier sample nos 1 and 11 were excluded from the analysis.
