Figure 7. DNA-RNA hybrid and strand specific mutation distribution RNA exosome substrate ncRNA expressing region of Pim1 and CD83 genes in the absence of Mtr4 and Setx.
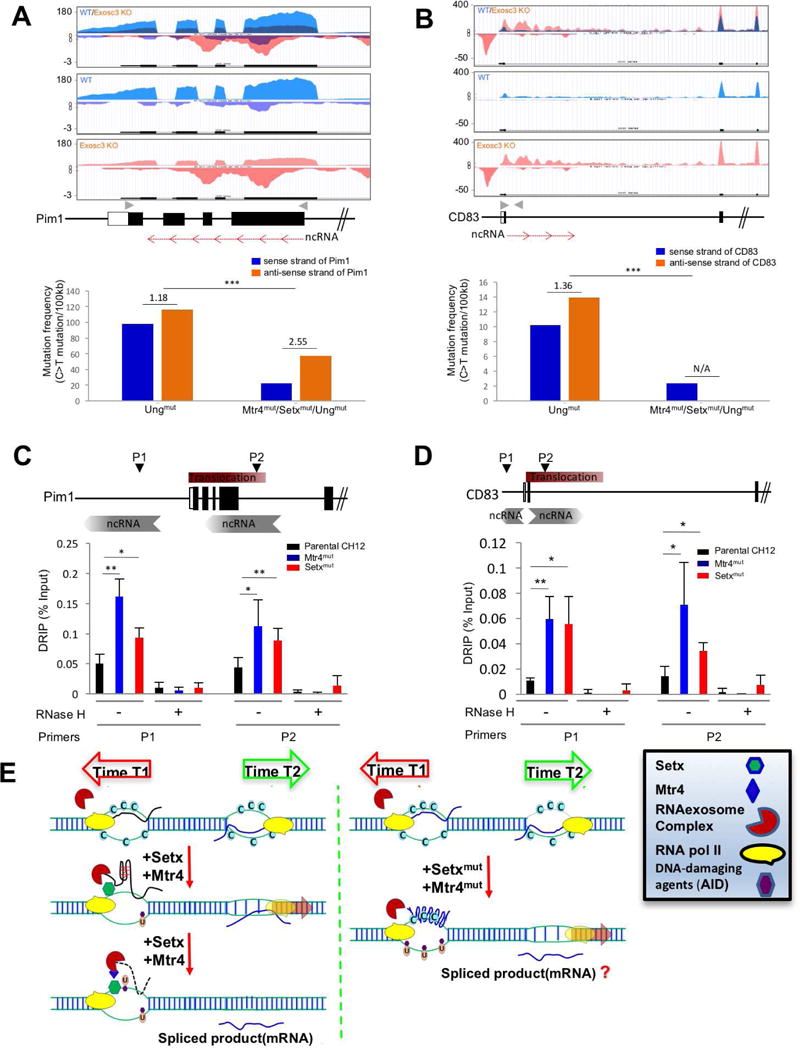
(A, B) RNA exosome substrate ncRNA expression profiles of Pim1 (A) and CD83 (B) loci in WT and Exosc3COIN/COIN mouse B cells (Top). Gray arrowheads indicate primer sites for next generation sequencing (NGS) and red arrows indicate non-coding RNA and its transcription direction on the schematic map of Pim1 and CD83 loci (Middle). Mutation frequency of C bases on sense and anti-sense strands (with respect to Pim1 or CD83 gene transcription in top panel) and ratio of sense strand mutation frequency compare to anti-sense (transcribed) strand mutation frequency in Ung mutant and Mtr4/Setx/Ung mutant CH12F3 cells. Ratio of mutation frequency between sense and anti-sense strand is indicated above bar graph (bottom). (C, D) Schematic map localizing the Pim1 (C) and CD83 (D) loci and binding sites of the primer pairs used for DNA-RNA hybrid immunoprecipitation (DRIP) assays. This experiment was performed as in Fig. 5D. (E) A model elucidating the role of Mtr4 and Setx in restricting ssDNA structure formation at various regions in the genome that have antisense RNA transcription or sense/antisense paired RNA transcription. Time 1 and time 2 represents two separate time points at which two RNAs are expressed inside a genic locus (e.g., Pim1 or CD83). The RNA processing of the two RNAs are potentially through two different mechanisms (e.g., splicing and RNA degradation, respectively). It is to be determined whether the efficient processing of the exosome sensitive ncRNA is important for proper mRNA biogenesis.
Error bars indicate S.D. (P-value: * < 0.05, ** <0.01, *** <0.001); A is obtained from ES cell transcriptome; details of mutations identified by NGS deep sequencing are presented in supplementary table 1c.
