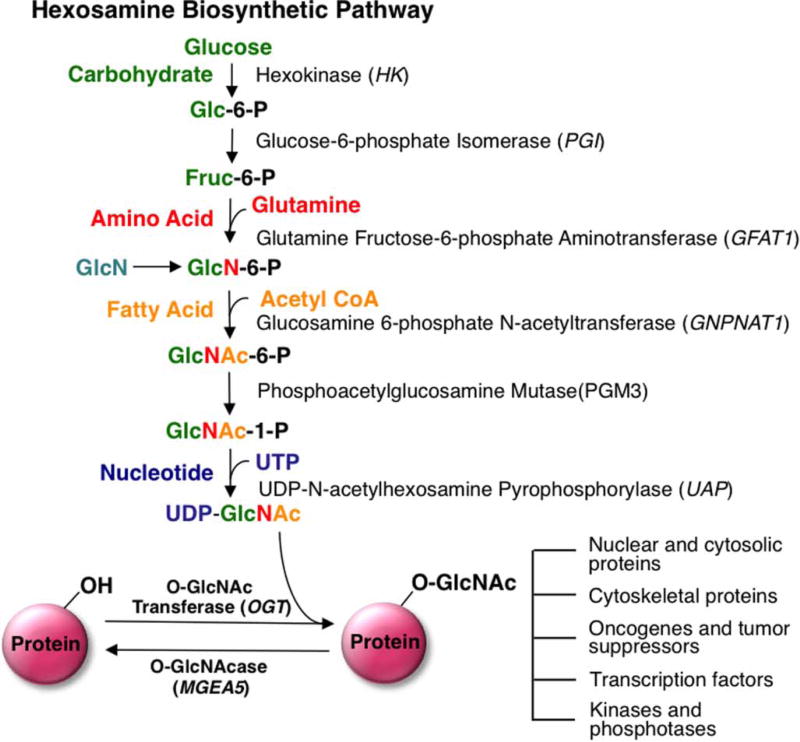
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the HBP and O-GlcNAc modification.
Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate (GFAT) is the rate-limiting step of the HBP pathway. GlcN treatment can bypass GFAT, causing an elevation in O-GlcNAcylation. The HBP is composed of various metabolic inputs including glucose, amino acid, fatty acid, and nucleotide metabolisms that ultimately serve to synthesize the donor substrate for OGT, UDP-GlcNAc. These metabolic inputs make O-GlcNAc a nutrient sensor capable of influencing many cellular processes including transcription, cell growth, and proliferation. Glc-6-P, glucose-6-phosphate; Fruc-6-P, fructose-6-phosphate; GlcN-6-P, glucosamine-6-phosphate; GlcNAc-6-P, N-acetylglucosamine-6-P; GlcNAc-1-P, N-acetylglucosamine-1-P. Arrow indicates that multiple steps are involved in the conversion.