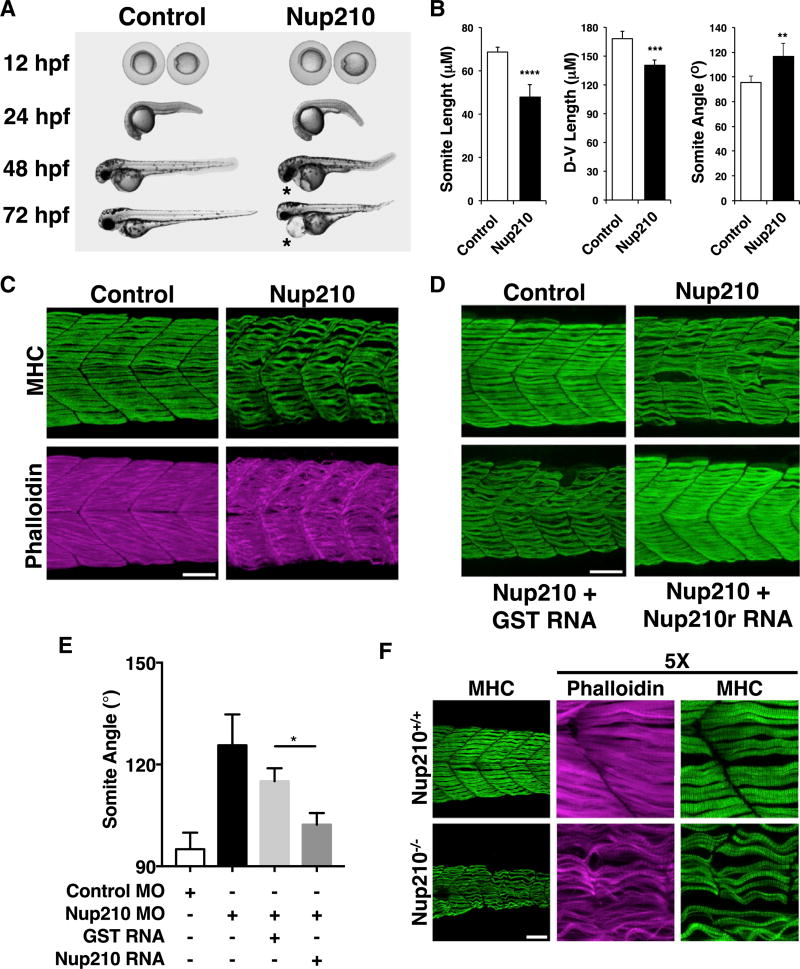
Figure 1. Nup210 Is Required for Skeletal Muscle Development.
(A) Zebrafish one-cell embryos injected with Control or Nup210 morpholinos (MO) were imaged at different times of development. Asterisks show cardiac edema.
(B) The length, height (dorsal-ventral length), and angle of somite #20 were quantified in control and Nup210-depleted animals stained with the F59 antibody.
(C) Zebrafish embryos injected with control or Nup210 MOs were stained with F59 and phalloidin at 48 hpf. Images represent the maximal projection of multiple z stacks.
(D) Embryos were co-injected with control or Nup210 morpholinos and GST mRNA, or a Nup210 mRNA resistant to the morpholino (Nup210r) and muscle was analyzed at 48 hpf.
(E) Rescue experiments from (D) were quantified by measuring somite angle.
(F) Muscle structure in Nup210 CRISPR knockouts was analyzed at 48 hpf by staining with F59 and phalloidin.
Bar plots represent mean ± SEM, n ≥ 3 replicates. *p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p ≤ 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t test. Morpholino depletions were performed with n ≥ 50 embryos. Ten to 20 embryos were examined by immunofluorescence and quantified in n ≥ 3 independent experiments. Scale bars, 50 µm. See also Figure S1.