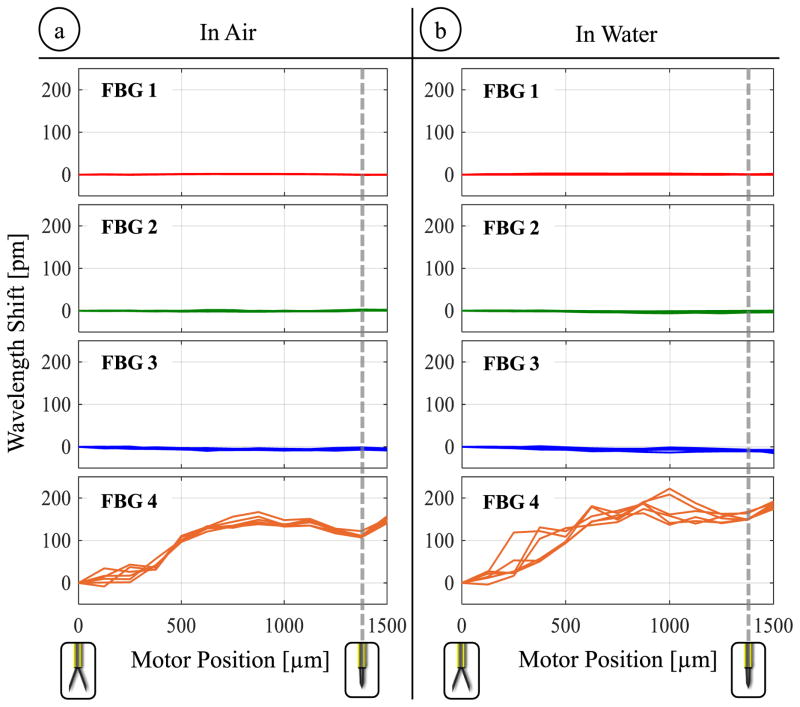
Fig. 7.
The effect of opening/closing the forceps on the lateral (FBG 1,2,3) and axial (FBG 4) sensors while operating (a) in air and (b) in water. The actuation induces high levels of wavelength shift on the axial sensor (up to 167 pm in air and up to 222 pm in water), which exhibit a consistent variation among repeated trials, and hence can be modeled as a function of motor position for each environment.