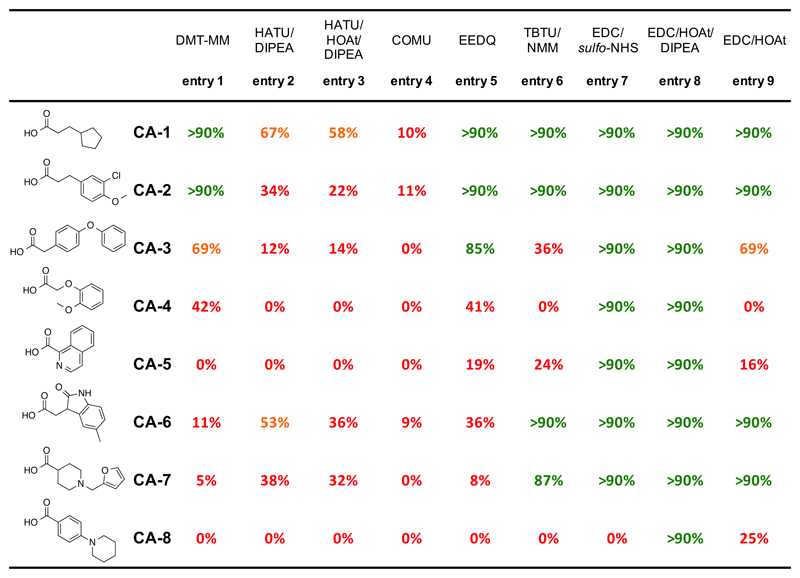
Figure 1.
Summary of coupling conversions by using different coupling reagents with eight representative carboxylic acids. In all cases, 72 μL ODN-1 (MOPS buffer pH 8.0, 0.5 nmol), 45 μL carboxylic acid (60 mM in DMSO) and coupling reagent were reacted for 16h at RT, followed by an additional coupling step with the same activated carboxylic acid for 6h at RT. Coupling reagents: entry 1: 4 μL DMT-MM (300 mM in water); entry 2: 4 μL HATU (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL DIPEA (300 mM in DMSO); entry 3: 4 μL HATU (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL HATU (60 mM in DMSO), 4 μL DIPEA (300 mM in DMSO); entry 4: 4 μL COMU (300 mM in DMSO); entry 5: 4 μL EEDQ (300 mM in DMSO); entry 6: 4 μL TBTU (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL NMM (300 mM in DMSO); entry 7: 4 μL EDC (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL sulfo-NHS (60 mM in DMSO:water = 2:1); entry 8: 4 μL EDC (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL HOAt (60 mM in DMSO), 4 μL DIPEA (300 mM in DMSO); entry 9: 4 μL EDC (300 mM in DMSO), 4 μL HOAt (60 mM in DMSO).