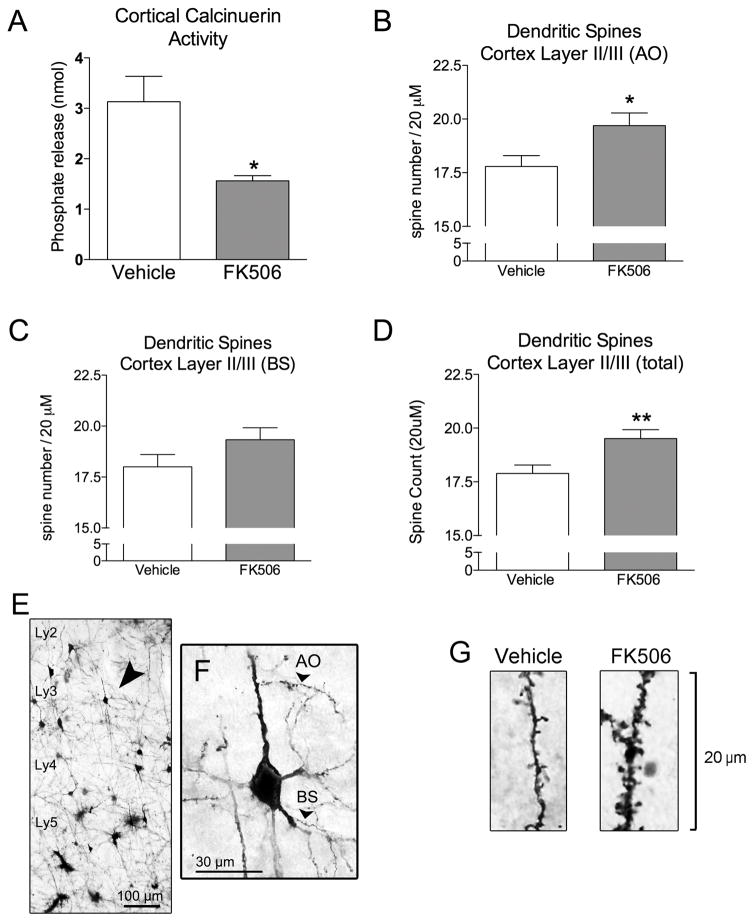
Figure 1. Calcineurin inhibition by FK506 causes dendritic spine growth in C57Bl/6 mice.
A) Four day peripheral administration of 100 mg/kg FK506 results in a decrease in calcineurin activity in the mouse cortex. B) Spine density quantification in the apical oblique (AO) dendrites, C) basal shaft (BS) dendrites, and D) total spine counts following four day vehicle or FK506 administration in mice. E–F) Golgi stained cortical section showing the layers of the cortex, and the areas of the dendrites where spines were quantified. G) Representative images of the Golgi stained AO dendrites spines following vehicle or FK506 treatment. Unpaired t-test. * = P < 0.05; ** = P < 0.01.