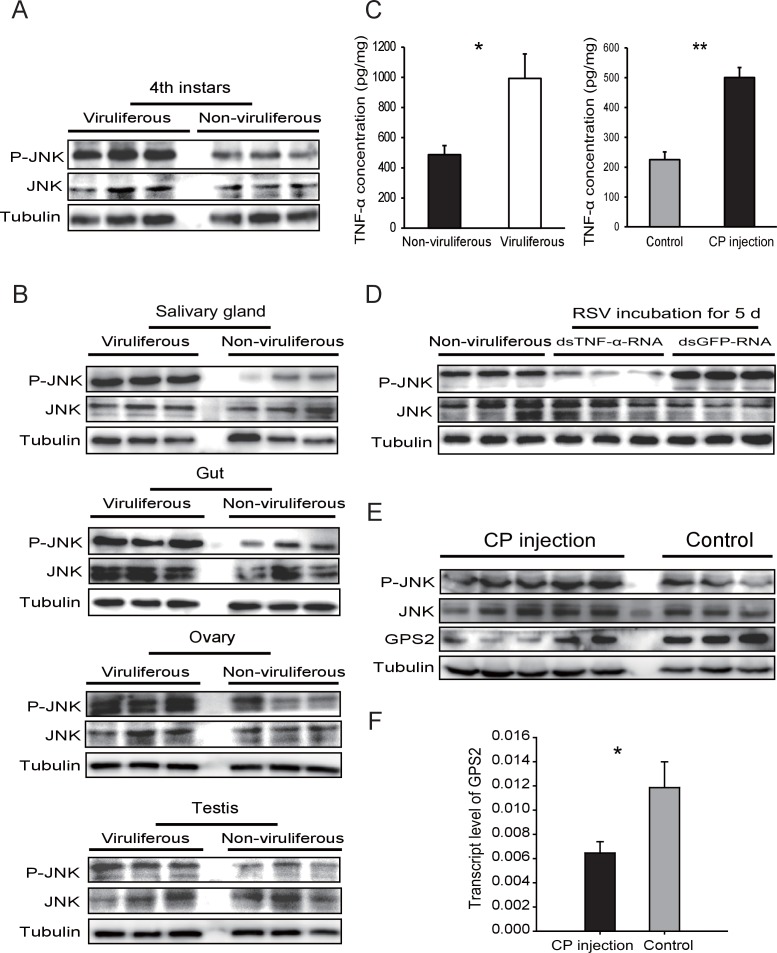
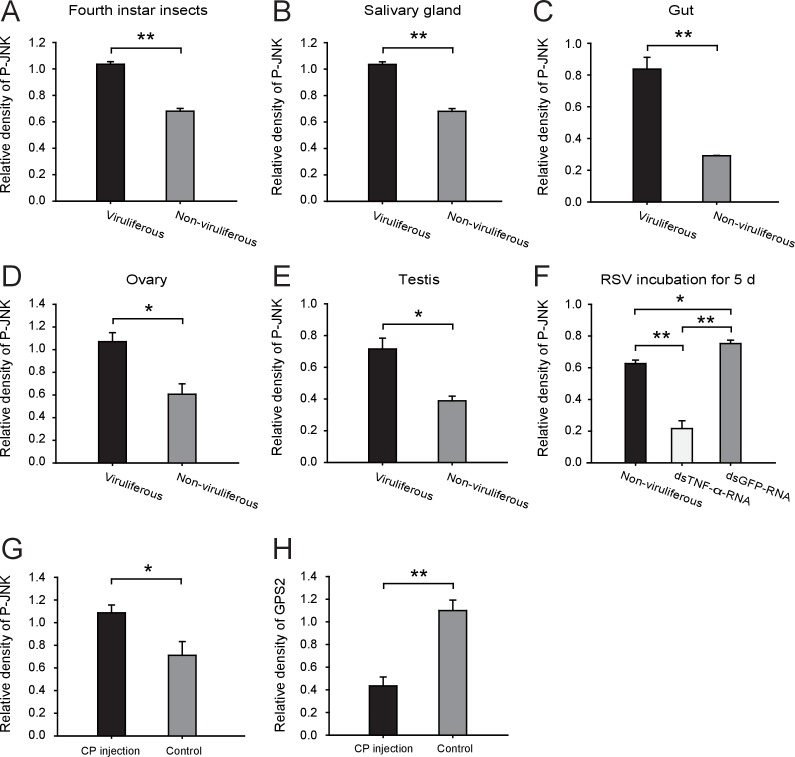
Figure 4. Rice stripe virus activates the JNK signaling pathway.
(A) Western blotting showing the phosphorylated JNK (P-JNK) in the fourth instar nymphs of viruliferous and non-viruliferous planthoppers. (B) Western blotting showing the P-JNK in salivary gland, gut, ovary, and testis of viruliferous and non-viruliferous planthoppers. (C) The TNF-α levels in the fourth instar nymphs of viruliferous and non-viruliferous planthoppers, or in CP-His-protein-injected non-viruliferous insects and negative control groups, determined using a human TNF-α ELISA Kit. (D) Western blotting showing the P-JNK in the fourth instar nymphs when dsTNF-α-RNA was injected and RSV was incubated in insects for five days. (E) Western blotting showing the P-JNK and GPS2 in non-viruliferous fourth instar nymphs at 24 hr after CP-His protein injection. The control insects were injected with purified products from pET28a vector. (F) Relative transcript levels of GPS2 after CP-His protein injection. The P-JNK, total JNK, GPS2, and tubulin were detected using an anti-phospho-human JNK2 polyclonal antibody, an anti-human JNK2 polyclonal antibody, an anti-human GPS2 polyclonal antibody, and an anti-human tubulin monoclonal antibody, respectively. *p<0.05; **p<0.01.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.26591.013