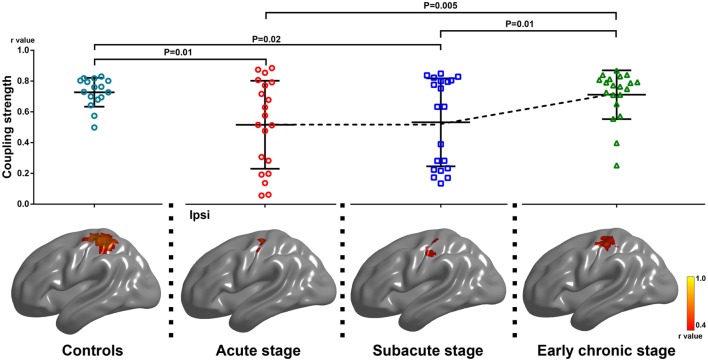
Figure 3.
Alterations of coupling strength between motion-related activation and resting-state functional connectivity within the group-specific mask in healthy controls and stroke patients among three stages of progression. Upper row: changes in coupling strength across the three stages (F = 6.81, P = 0.003, one-way repeated measures analysis of variance). Compared with the acute and subacute stages, the degree of coupling increased significantly during the early chronic stage (P = 0.005, P = 0.01, respectively; post hoc test). Compared with healthy controls, stroke patients showed reduced motion-related activation and coupling strength during the acute and subacute stages (P = 0.01, P = 0.02, respectively; two-sample t test). Lower row: the results arising from our cross-subject correlation analysis within the group-specific mask in healthy controls and stroke patients across the three stages of progression. The level of significant voxel clearly increased during the early chronic stage. Ipsi, the ipsilesional hemisphere.