Figure 3.
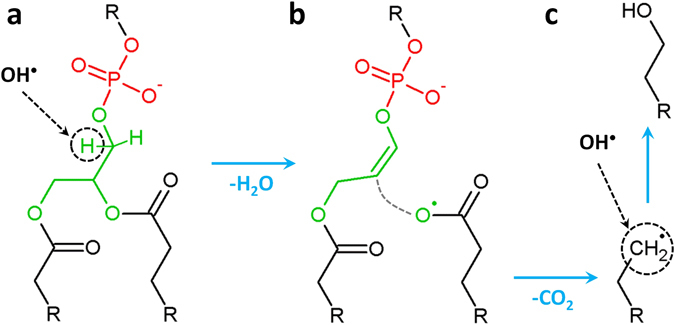
Breaking mechanism of a C-O bond upon impact of an OH radical. The OH radical abstracts a H atom (see black dashed circle in (a)) leading to the formation of a water molecule. This subsequently results in the formation of a double C=C bond, the cleavage of a C-O bond (see gray dashed line in (b)) and the detachment of a CO2 molecule, leaving behind a radical site (see black dashed circle in (c)). A new OH radical can then react with this site, forming an alcohol group (c).
