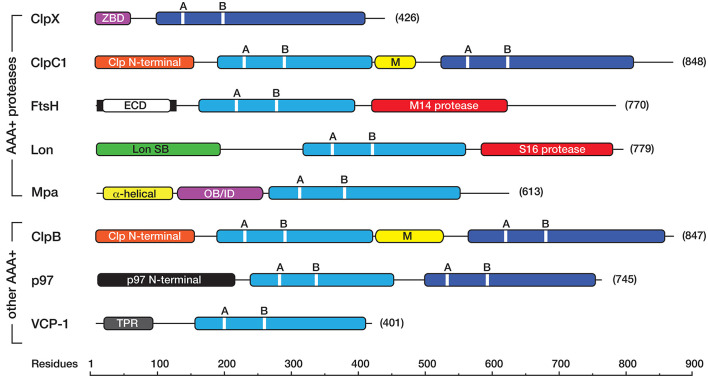
Figure 1.
Linear cartoon of the different AAA+ proteins in mycobacteria, illustrating the position of various domains and motifs. The AAA+ domains either belong to the classic (light blue) or HCLR (dark blue) clade. Each AAA+ domain contains a consensus sequence for ATP binding (GX4GKT/S, where X is any amino acid) and hydrolysis (hDD/E, where h is any hydrophobic amino acid) known as the Walker A (A), and Walker B (B) motifs, respectively. Most AAA+ proteins contain an unique accessory domain, such as the zinc-binding domain (ZBD, in pink) in ClpX, the Clp N-terminal domain (orange) in ClpC1 and ClpB, the Lon SB (substrate binding) domain (green) in Lon, the α-helical (yellow) and OB/ID (pink) domains in Mpa, the p97 N-terminal domain (black) in Msm0858 and the Tetratricopeptide (TPR)-like domain (gray) in VCP-1. ClpC1 and ClpB also contain a middle (M) domain (yellow) located between the first and second AAA+ domain. The membrane-bound AAA+ protein, FtsH contains two transmembrane domains (black bars) separated by an extracellular domain (ECD, in white) and a C-terminal metallopeptidase (M14 peptidase) domain (red) containing the consensus sequence (HEXGH). Lon contains an N-terminal substrate binding (Lon SB) domain a central AAA+ domain and a C-terminal serine (S16) peptidase domain (red) with the catalytic dyad (S, K). All cartoons are derived from the sequences for the following M. smegmatis proteins ClpX (A0R196), ClpC1 (A0R574), FtsH (A0R588), Lon (O31147), Mpa (A0QZ54), ClpB (A0QQF0), p97/Msm0858 (A0QQS4), VCP-1/Msm1854 (A0QTI2). Domains (and domain boundaries) were defined by InterPro (EMBL-EBI) as follows: AAA+ (IPR003593); C4-type Zinc finger (IPR010603); Clp N-terminal (IPR004176); UVR or M (IPR001943); Lon SB (substrate binding) (IPR003111); p97 N-terminal (IPR003338); p97 OB/ID (IPR032501); Tetratricopeptide (TPR)-like (IPR011990); S16 protease (IPR008269), M41 protease (IPR000642).