Figure 5.
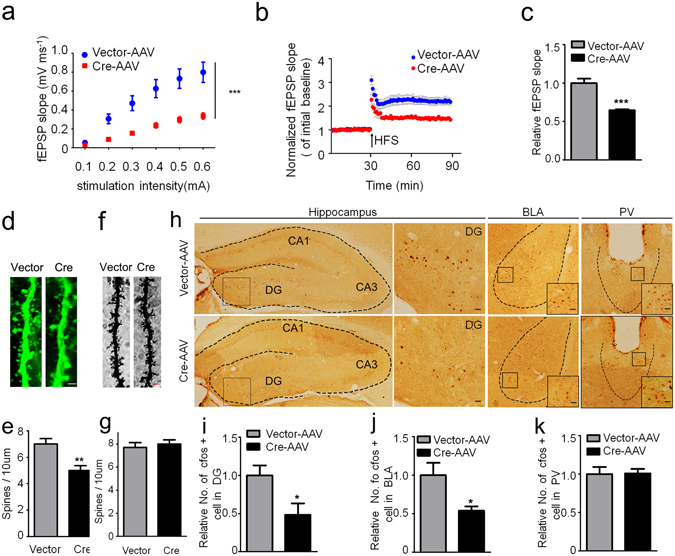
GSK-3β deletion inhibits activity-dependent neural activation. (a) GSK-3β deletion significantly suppressed basal synaptic transmission shown by the reduced input/output (I/O) curve. (b,c) GSK-3β deletion induced LTP impairment shown by a decreased slop of the evoked fEPSP, and the decrease was still significant at 60 min after high frequency stimulation (HFS). n = 8–10 hippocampal slices from 6 mice in each group. (d,e) The representative micrographs of spine morphology and the decreased spine density in GFP-positive neurons (6 mice were analyzed in each group). (f,g) The representative micrographs of spine morphology and the spine density in prefrontal cortex neurons (6 mice were analyzed in each group). (h–k) The representative immunohistochemical images of c-fos, and the densitometric analyses in DG (dentate gyrus), BLA (basal lateral amygdala) and PV (paraventricular thalamic nucleus) subsets (Scale bars, 20 μm; n = 5–6 each group). Data were presented as mean ± s.e.m. Two–way repeated-measures ANOVA with Huynh-Feldt-Lecoutre correction for panels (a), unpaired t test for panels (c,e,i–k). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001 versus Vector. The absence of asterix indicates that the difference is not significant.
