Figure 3.
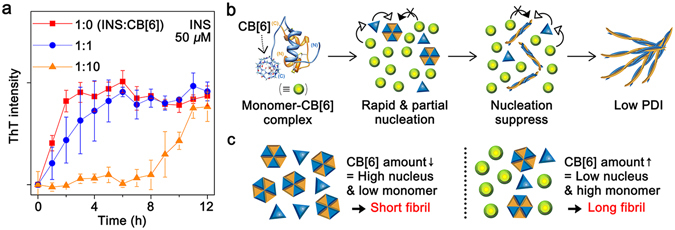
Fibrillation mechanism controlled by CB[6]. (a) Thioflavin T (ThT) assay for the kinetics of INS fibrillation with various amounts of CB[6] in solution (INS = 50 μM). The 5 mM CB[6] condition was excluded because of the turbidity of CB[6] in the solution. (b) Schematic representation for CB[6]-mediated kinetic control in nucleation. (c) Correlation between fibril length and monomer:nucleus ratio. As the amount of CB[6] decreases (left) or increases (right), the fibril length is shortened or lengthened, respectively.
