Figure 1.
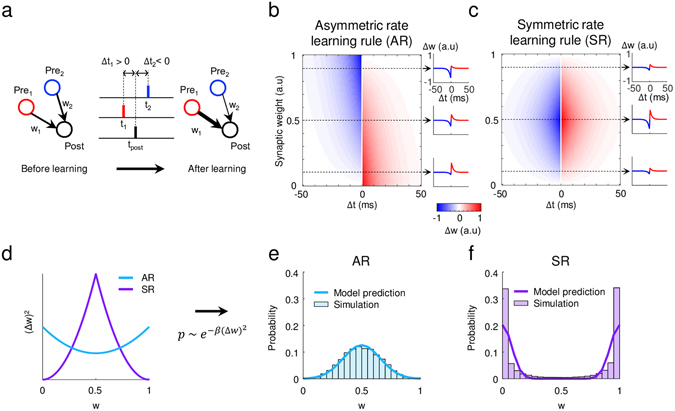
Weight-dependent learning rules: (a) A model of spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP). Synaptic strength change (Δw) depends on the relative spike timing between pre- and postsynaptic neurons (Δt). Spikes of Δt > 0 leads to long term potentiation (LTP), while spike of Δt < 0 leads to long-term depression (LTD). (b) Asymmetric learning rate (AR) model: Learning rates for LTP (red) and LTD (blue) are asymmetric for strong and weak synapses. (c) Symmetric learning rate (SR) model: Learning rates for LTP (red) and LTD (blue) are symmetric for strong and weak synapses. (d) Instability of the synapses (Δw2) for AR and SR models. (e,f) Weight density function for AR and SR was predicted from Boltzmann distribution (colored lines), and simulated using a single synapse model (histograms).
