Figure 2.
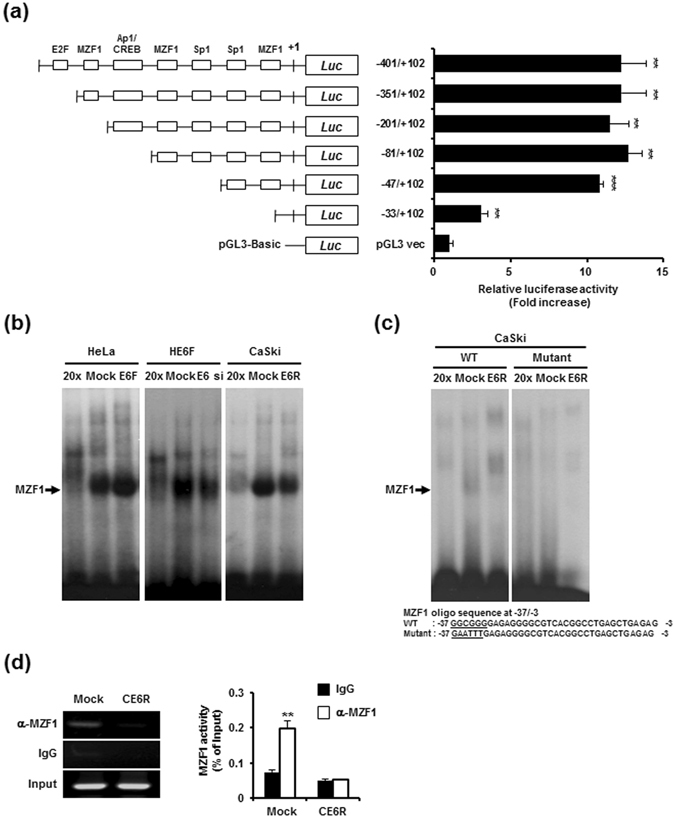
Transcriptional activation of MZF1 in the regulation of E6-mediated Axl expression. (a) Luciferase assays of lysates from 293 T cells following co-transfection with Axl promoter deletion constructs and a plasmid encoding HPV16E6 as indicated. Data are the mean ± s.e.m. from three independent experiments (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). (b) MZF1 DNA binding ability was analysed by EMSA using nuclear extracts obtained from HE6F (left), E6-silenced HE6F (middle), and CE6R (right) cells and corresponding mock controls. Oct-1 was used as an internal control for equal protein loading. Cold 20 × contains a 20-fold excess of unlabelled MZF1 probe for competition analysis. (c) EMSA was done with oligonucleotides specific for MZF1 binding motif at −37/−3 bp or with mutated sequence of MZF1. (d) DNA-protein complexes were immunoprecipitated from cross-linked chromatin using antibody specific for MZF1 and normal IgG control. The immunoprecipitated chromatin was subjected to PCR analysis using the indicated primers (left), and the binding activity was represented as a bar graph after calculating a relative percentage compared with corresponding levels in input DNA (right panel). The graphs represent the mean ± standard deviation of triplicate determinations (**P < 0.01).
