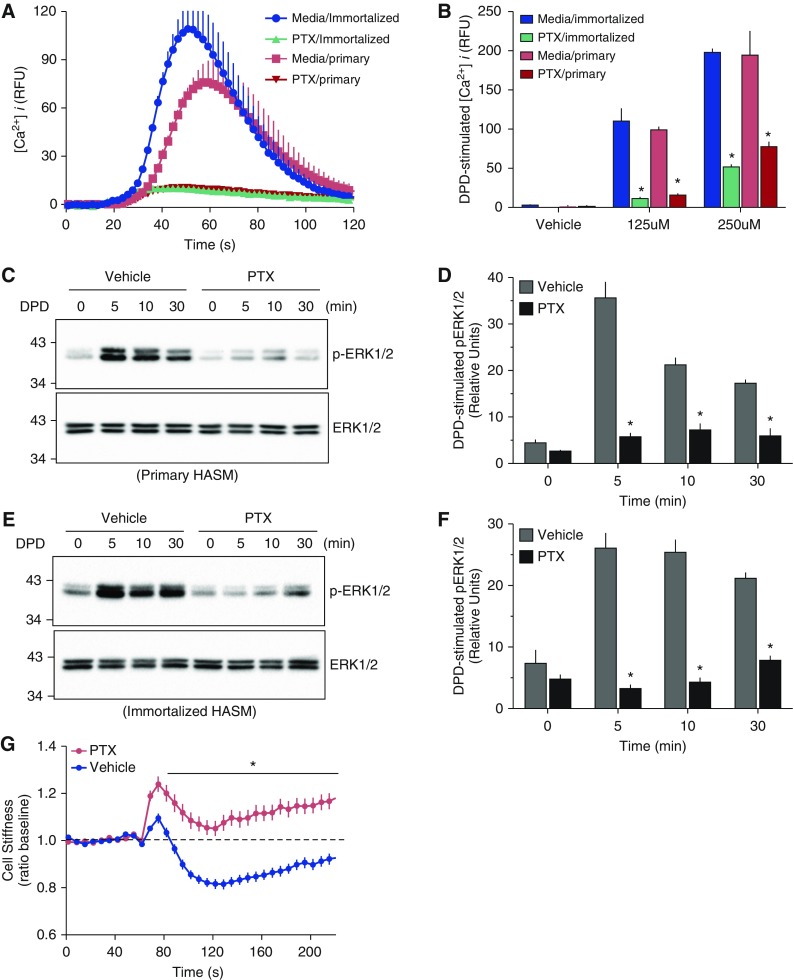
Figure 1.
Bitter taste receptor (TAS2R) function in human airway smooth muscle (HASM) is inhibited by pertussis toxin (PTX). Primary HASM cells or D9 immortalized HASM cells were treated with media alone or media with 0.5 μg PTX for 24 hours, and the intracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) response to 250 μM of the TAS2R14 agonist diphenhydramine (DPD) or vehicle was determined. (A) Representative tracings in which DPD or vehicle was added at the 19-second time point. (B) The mean (±SE) results of the peak [Ca2+]i from five experiments, *P < 0.01 PTX versus media alone treatment. (C and E) Representative Western blots of phospho–extracellular signal–regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 and total ERK1/2 in response to 500 μM DPD from 0 to 30 minutes. (D and F) Mean (±SE) of the phospho-ERK1/2 responses from four experiments, *P < 0.01 PTX versus media. (G) Physiologic response of primary HASM to 250 μM DPD in the absence or presence of PTX pretreatment, as determined by magnetic twisting cytometry. Results are mean (±SE) from 445 to 466 measurements from cells from 4 different culture wells. *P < 0.001 PTX versus vehicle. RFU, relative fluorescent units.