Table 6.
The structures, physicochemical properties, and mechanisms of the novel TLR nano-inhibitors.
| Compound | NAHNP | HDL-like NP | Bare GNP | Glycolipid-coated GNP | Peptide-GNP hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | 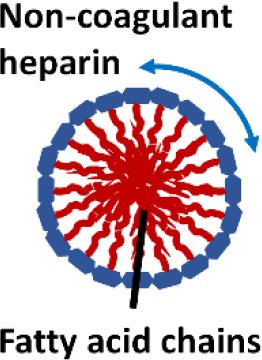 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
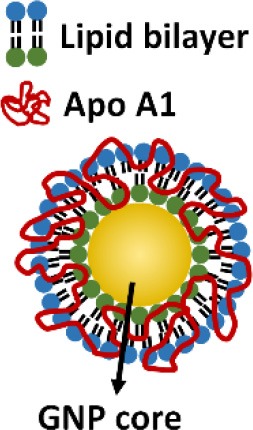
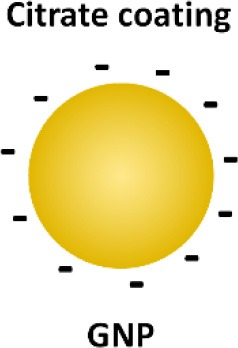
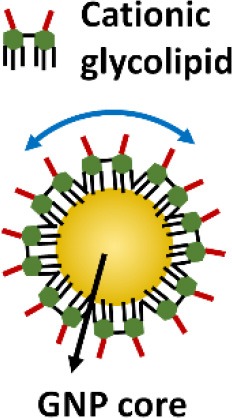
| Size | 110–160 nm | ~15 nm | ~30 nm | N/A | ~15 nm |
| NP formation | Self-assembling | Surface coating on GNP | GNP only (citrate coated) | Surface coating on GNP | Surface coating on GNP |
| Surface charge | Negative | Negative | Negative | Positive | Negative |
| Biodegradability | Possible | No | No | No | No |
| Mechanisms of action | Interaction with TLR4/MD2 complex | Neutralization of LPS | Decrease in TLR4 and NF-κB expression | Binding to TLR/MD2 complex | Endosomal pH modulation |
| Inhibiting MyD88-dependent NF-κB pathway | Inhibiting LPS induced NF-κB signaling | Inhibiting LPS induced NF-κB signaling | Inhibiting both NF-κB and IRF pathways | ||
| References | Babazada et al., 2014a,b | Foit and Thaxton, 2016 | Pereira et al., 2012 | Rodriguez Lavado et al., 2014 | Yang et al., 2015, 2016 |
NAHNP, non-anticoagulant heparin nanoparticle; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; NP, nanoparticle; GNP, gold nanoparticle; Apo A1, apolipoprotein A1; N/A, not available.
