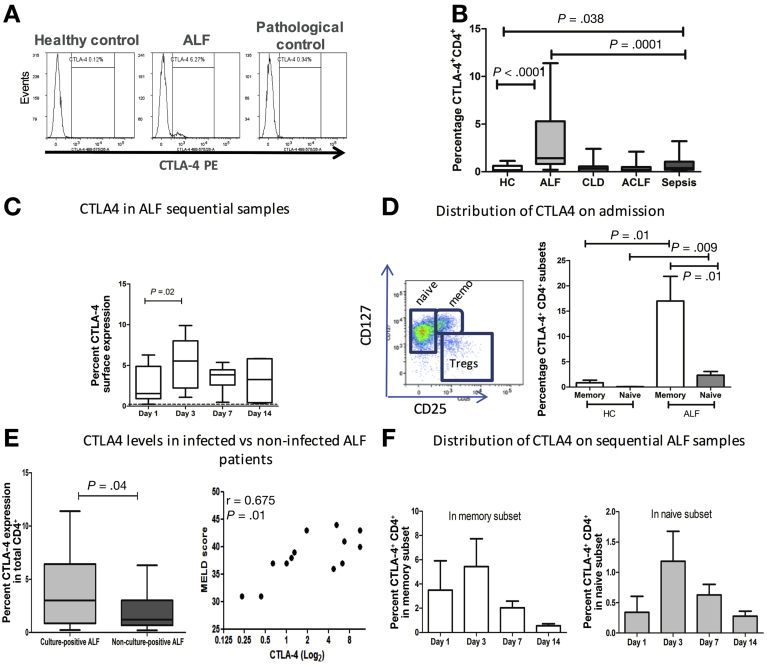
Figure 2.
Percentages of CTLA4-expressing CD4+ T cells are elevated in ALF patients. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots to determine CTLA4-expressing CD4+ T cells in HC (left), ALF (middle), and pathologic controls (right). (B) Data show that percentages of circulating CD4+ T cells expressing CTLA4 are significantly elevated in ALF compared to HCs (P < .0001). (C) CTLA4 levels were determined in sequential samples at days 3 (n = 7), 7 (n = 8), and 14 (n = 5) after admission and compared to HC levels, represented by the dashed line. (D) Left: Representative plot to define CD3+CD4+ regulatory T cells, naïve, and memory subsets using CD25 and CD127 markers. Right: Distribution of CTLA4 expression in different CD4+ T cell subsets, mainly naïve and memory subsets on day 1 of submission (n = 15). (E) CTLA4 expression was assessed in ALF patients who developed infections (n = 11) and the ones who did not develop infections (n = 23). (F) Distribution of CTLA4+CD4+ among memory and naïve T-cell subsets assessed in longitudinal samples on days 1 (n = 6), 3 (n = 7), 7 (n = 8), and 14 (n = 5) after admission.