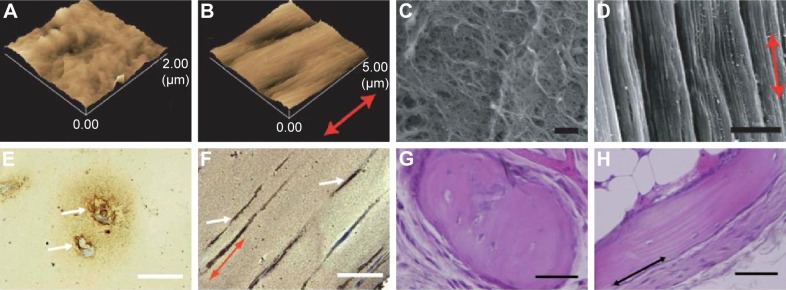
Figure 3.
AFM images of a control fibrin gel (A) and a strained fibrin gel (B). Scanning electron microscopy images of a control fibrin gel (C) (bar: 1 µm) and bundle-like structures formed in a strained fibrin gel (D) (bar: 5 µm). Reproduced from Matsumoto T, Sasaki J-I, Alsberg E, Egusa H, Yatani H, Sohmura T. Three-dimensional cell and tissue patterning in a strained fibrin gel system. PLoS One. 2007;2(11):e1211.77 Mineral depositions of contained mouse BMSCs detected by von Kossa staining of a control gel (E) and strained gel (F) (bar: 50 µm). Reproduced from78 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry. H&E stained images of ectopic bone formation by nonstatic (G) and static (H) fibrin gels. Implanted fibrin gels were harvested at 6 weeks after implantation in mice (bar: 50 µm). Reproduced from Sasaki JI, Matsumoto T, Imazato S. Oriented bone formation using biomimetic fibrin hydrogels with three-dimensional patterned bone matrices. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(2):622–627.79 The arrows indicate the mechanical force direction.
Abbreviations: AFM, atomic force microscopy; BMSCs, bone marrow-derived stromal cells; H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.