Figure 3. LLS2 causes membrane dissociation of H-and K-Ras.
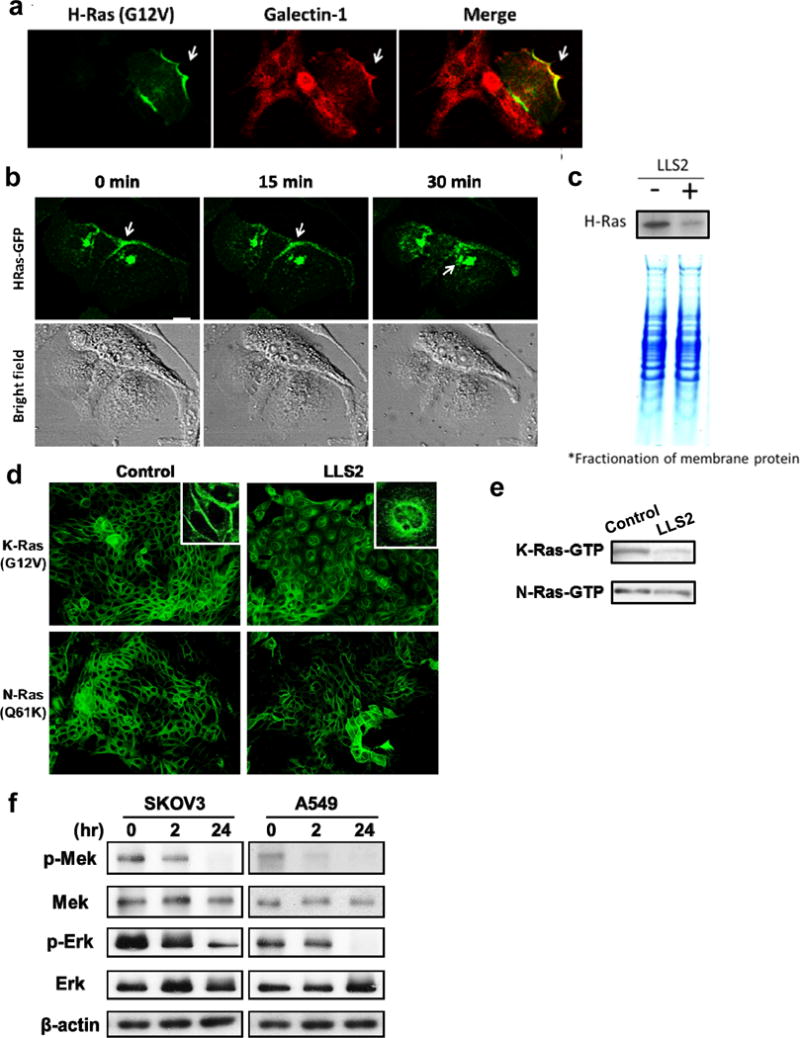
(a) Co-localization of galectin-1 and H-Ras. (b) Once activated by EGF, H-Ras will be partially trafficked to the plasma membrane leading to the activation of Erk pathway. After 15 mins treatment with LLS2(25 μM), there was a loss of membrane-localized H-Ras. Notably, intracellular H-Ras was augmented 30 mins after LLS2 treatment. Scale bars: 25 μm. (c) Quantification of membrane associated H-Ras (active form) by immunoblot analysis after treatment with buffer (−) or LLS2 (+), showing that LLS2 was able to lower the level of activated H- and K-Ras. (d) LLS2 also miscolocalized the EGF-stimulated K-Ras(G12V) but not N-Ras(Q61K). (e) Quantification of activated K- and N-Ras. (f) phospho-Mek and phospho-Erk were significantly down-regulated after treatment with LLS2 (25 μM) for 24 hours. Scale bars: 50 μm.
