Figure 3. The serine biosynthesis pathway and extensions to the one-carbon metabolism, the methionine cycle, the purine biosynthesis pathway and the generation of glutathione.
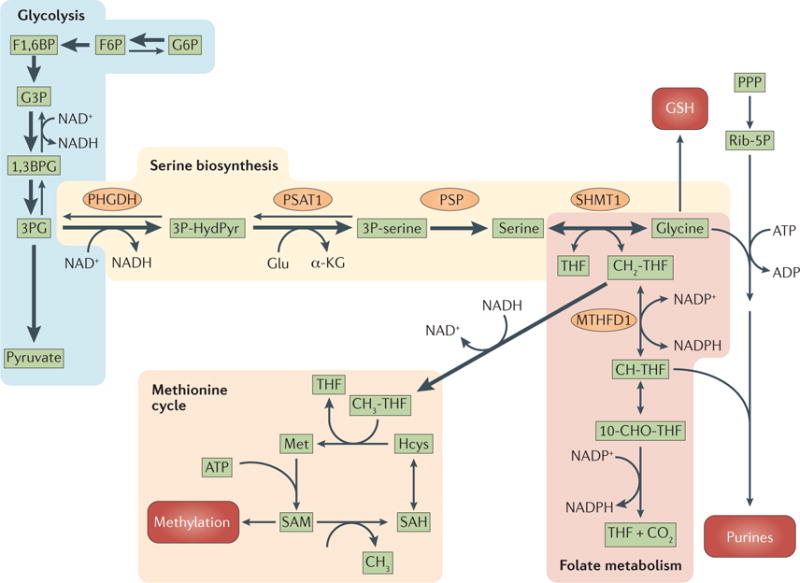
3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) generated by glycolysis provides the initial substrate for serine biosynthesis. In the first step in the serine biosynthesis pathway, 3PG is oxidized by phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) in a reaction that consumes NAD+. The second step is catalysed by phosphoserine aminotransferase (PSAT1) in a reaction that is coupled to deamination of glutamate (Glu) to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). The last step is catalysed by phosphoserine phosphatase (PSP). The conversion of serine to glycine generates 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (CH2-THF), which is then used in folate metabolism and in the methionine cycle. Glycine is used to generate glutathione (GSH), and together with ribose-5-phosphate (Rib-5P) to generate purines. The folate pathway can generate NADPH, and 10-formyl-THF (10-CHO-THF). 10-CHO-THF together with Rib-5P and glycine participates in the generation of purines. Demethylation of 5-methyl-THF (CH3-THF) contributes one carbon to the methionine cycle by the methylation of homocysteine (Hcys) to generate methionine (Met). Methionine is converted into S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and is used by methyltransferases. Demethylation of SAM generates S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH), which is converted back into Hcys by deadenylation. The thickness of the arrows indicatesrelative flux. 1,3BPG, 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate; 3P-HydPyr, 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate; 3P-serine, 3-phosphoserine; CH-THF, 5,10 methenyl-THF; F1,6BP, fructose-1,6-bisphosphate; F6P, fructose-6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; MTHFD1, methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 1; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; SHMT1, serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1.
