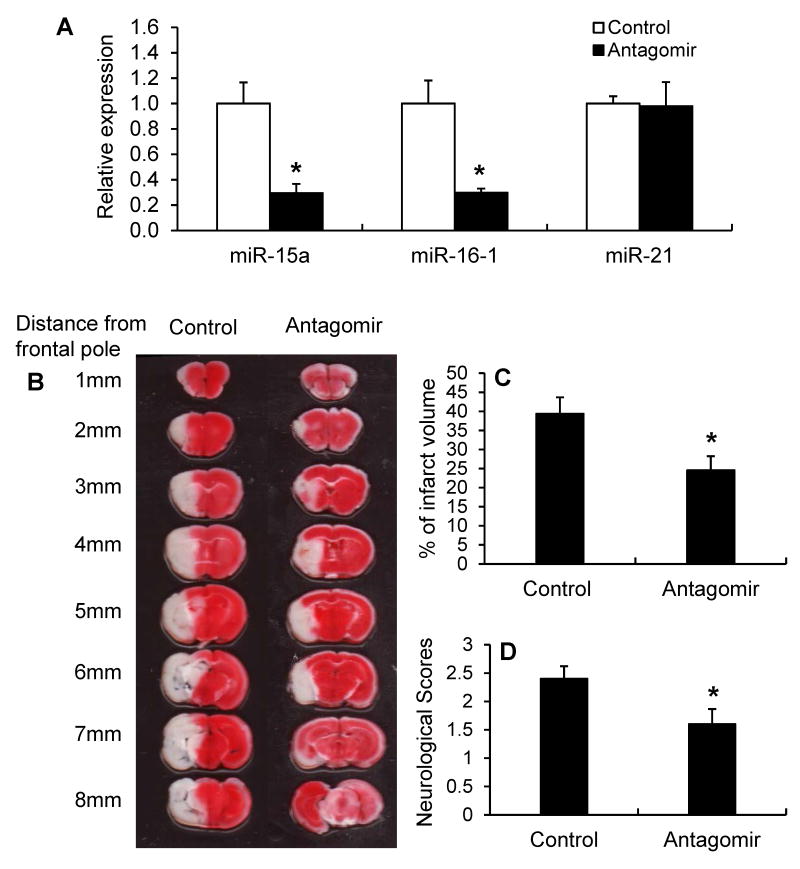
Figure 2.
The effect of miR-15a/16-1 antagomir on ischemic brain infarct and neurological outcome. C57BL/6J mice were subjected to 1h MCAO and 72h reperfusion. Mice were also subjected to intravenous (tail vein) injection of the miR-15a/16-1 specific antagomir (30 pmol/g) or scramble control (30 pmol/g) immediately after onset of MCAO. (A) Quantitative PCR data demonstrates that miR-15a and miR-16-1 expression were significantly inhibited in the cerebral cortex of mice after 1h MCAO and 72h reperfusion (n=3). Systematic treatment with miR-15a/16-1 antagomir had no effects on cerebral miR-21 expression. (B) 2% TTC-stained coronal sections are shown at different brain levels from posterior to the frontal pole from scramble-control treated ischemic mice and ischemic mice injected with miR-15a/16-1 antigomir. Infarct volume (C) and neurological deficits (D) were quantitatively assessed in mice after cerebral ischemia. Compared to antagomir control group, miR-15a/16-1 antagomir-treated mice showed smaller ischemia-induced brain infarct volume (n=10) and improved neurological outcomes (n=10). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 vs antagomir control group.