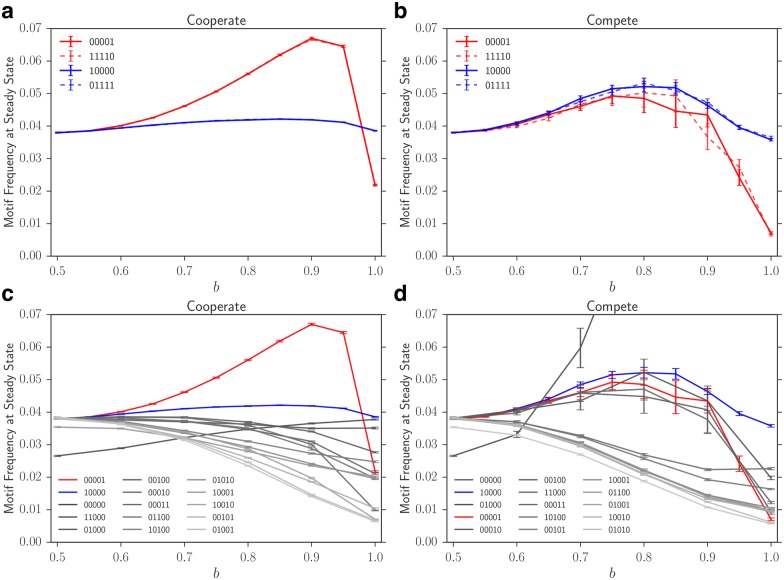
Fig 4. Steady state motif frequencies in cooperative and competitive dynamics.
Steady state frequency of motif-containing strands as a function of the bias in cooperative and competitive dynamics. In all cases, r = 0.05. Motif steady state distributions are the average of 50 trials. The values of b are shown for the motif that promotes the creation of 0 monomers (11110 and 01111 in subfigures (a) and (c), 00001 and 10000 in subfigures (b) and (d)). The other strands in the same subfigure promote 1 monomers with probability 1 − b. Shown are steady state motif frequencies for (a) The pairs A: 11110 and B: 00001 (in red) and A: 01111 and B: 10000 (in blue) under cooperation, (b) The pairs A: 11110 and B: 00001 (in red) and A: 01111 and B: 10000 (in blue) under competition, (c) all possible mirrored motif pairs of length 5 in the cooperating case (only one of the pair is shown since the two strands that make up the pair were indistinguishable from each other on average), and (d) all possible mirrored motif pairs of length 5 in the competition case. Note that in (d), the pair A: 00000 and B: 11111 grows much faster in comparison to the other pairs, and its behavior at high bias is not shown in order to make differences between other pairs more clear.