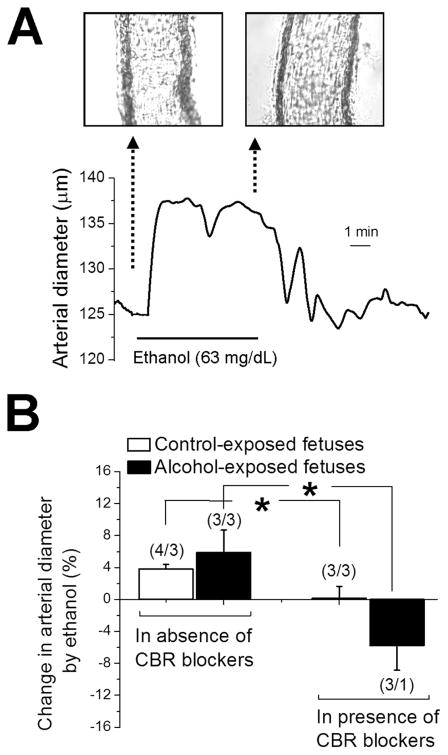
Fig. 3. Ethanol-induced dilation of in vitro pressurized fetal MCA.
A. Trace showing fetal cerebral artery dilation in response to 63-mg/dL ethanol. B. Bar graph displays averaged data: ethanol-induced dilation of fetal cerebral artery vanishes in presence of CB1 and CB2 receptor blockers AM251 and AM630, respectively. Data from control- and alcohol-exposed fetuses were compared using independent unpaired t tests. *Significantly different from data in absence of CBR blockers, p < 0.05. (n/N) = number of artery segments/number of fetuses.