Figure 4. AR antagonists synergize with everolimus to inhibit BC proliferation in vitro.
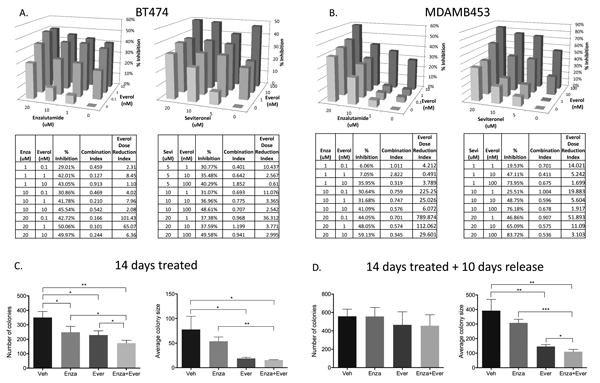
(A) BT474 and (B) MDAMB453 cells were labeled with nuclear red fluorescent protein and treated with Everol and either Enza or Sevi at doses indicated for six days in biological triplicate, and repeated at least twice. Proliferation was measured on an IncuCyte live cell imager using nuclear-RFP and percent confluence. Percent inhibition of growth was used to calculate synergistic interaction between the two drugs, using CalcuSyn software. A combination index (CI) <0.9 indicates synergy at a given dose combination, CI 0.9-1.1 indicates additivity, and CI>1.1 indicates antagonism. Everolimus Dose Reduction Index indicates the fold-change by which everolimus dose could be reduced when given in combination, as compared to Everol alone. (C) 2D colony formation assay of BT474-HR20 cells treated with 10uM Enza, 10nM Everol, or combination for two weeks, then (D) taken off treatment for an additional ten days and allowed to regrow. Colony formation assays were performed in biological triplicate *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
