Figure 2.
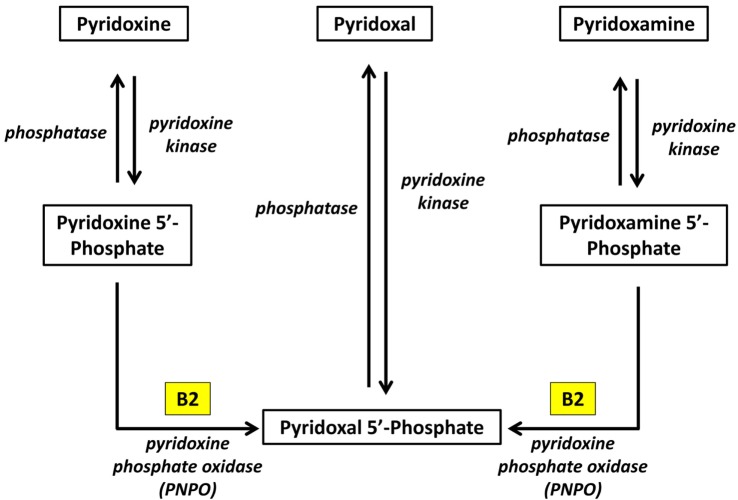
Riboflavin is required for the formation of Pyridoxal phosphate (68). Pyridoxine, pyridoxal, and pyridoxamine are forms of vitamin B6 (vitamin B6 vitamers). Through pyridoxine kinase, those vitamers will form pyridoxine 5′-phosphate, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate, respectively. These reactions are reversible with phosphatases. Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (PLP) is the active form of vitamin B6. Consequently, pyridoxine 5′-phosphate and pyridoxamine 5′-phosphate must be converted to PLP. Pyridoxine phosphate oxidase (PNPO) is the enzyme required for this conversion and formation of the active PLP from pyridoxine and pyridoxamine. PNPO requires riboflavin (B2) as its main cofactor.