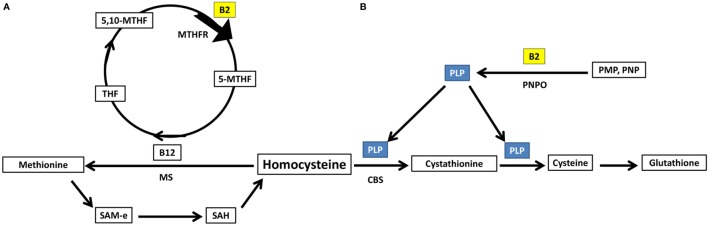
Figure 4.
Riboflavin has essential role in homocysteine metabolic pathways of re-methylation and transsulfuration. (A) Homocysteine undergoes re-methylation forming methionine through MS which requires methylated b12. The methyl group is donated from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate, synthesized via action of the riboflavin-dependent enzyme MTHFR on 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate. (B) The second fate of homocysteine is to undergo transsulfuration through CBS forming cystathionine and glutathione. This pathway requires PLP as a cofactor. PLP requires riboflavin for its synthesis from vitamin B6 phosphorylated vitamers. THF, tetrahydrofolate; 5,10-MTHF, 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate; MTHFR, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; 5-MTHF, 5-methyltetrahydrofolate; B12, cobalamin; MS, methionine synthase; SAM-e, S-adenosyl methionine; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; PLP, pyridoxal phosphate; CBS, cystathionine b-synthase; PNPO, pyridoxine/pyridoxamine phosphate oxidase; PMP, pyridoxamine phosphate; PNP, pyridoxine phosphate.