Figure 8.
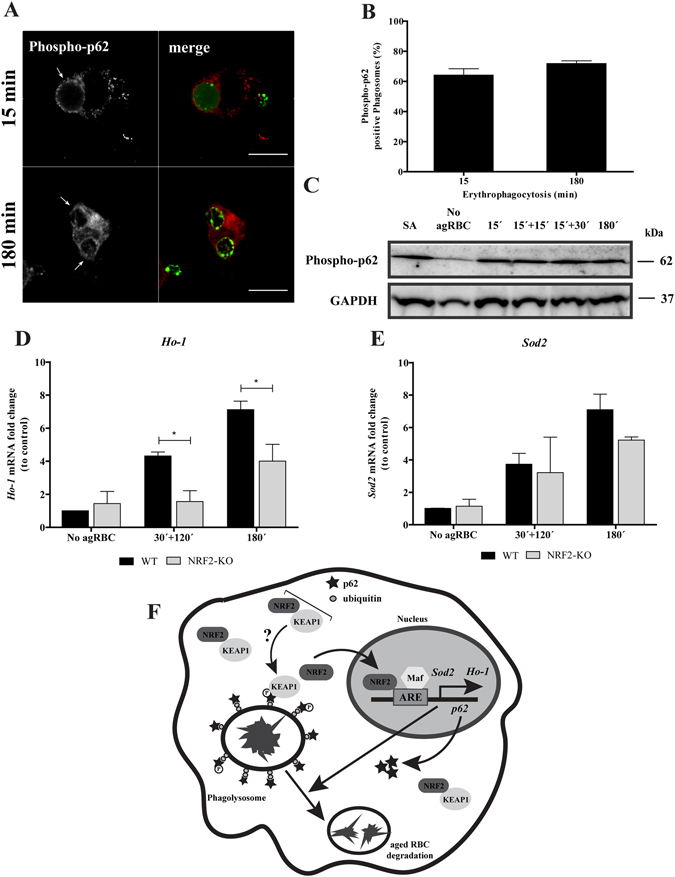
p62 Phosphorylation and NRF2-target genes expression upon erythrophagocytosis. WT-BMDM were fed and chased with CFSE-labeled RBC for the times indicated and imunostained for phospho-p62 (A,B) Quantification of phosphorylated p62-positive phagosomes. The values are means ± SEM expression levels of 2 independent experiments. (C) phosphorylated-p62 levels in cell lysates exposed to RBC. GAPDH was used as loading control. Two independent experiments were performed. As positive control, Sodium arsenite was added for 12 h to a final concentration of 10 µM. In D-E, WT- and NRF2-KO-BMDM were challenged with RBC for 30 min and then chased for 120 min or fed for 180 min. The expression of HO-1 (D), SOD2 (E) genes was assessed by RT-qPCR. Data were normalized to the endogenous Hprt and Pgk1 genes. The values are means ± SEM expression levels of three independent experiments, each measured in two technical replicates. *p < 0.05. (F) Working Model: Our model suggests that degradation of RBC by macrophages is dependent on p62/NRF2 signaling pathway. p62 is recruited to RBC-containing phagosomes decorated with ubiquitin shortly after erythrophagocytosis, followed by phosphorylation in the S351 residue and KEAP1 acquisition, by an unknown mechanism. Then, after phagolysosome formation NRF2 is translocated to the nucleus where together with small Maf proteins, binds to ARE in promoter region of Ho-1, p62 and Sod2 genes, inducing their expression. This molecular machinery promotes aged RBC degradation and controls oxidative stress. NRF2 - nuclear factor erythroid derived 2-like 2; KEAP1 - Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; ARE – antioxidant response element; Maf - small masculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma; Sod2 - superoxide dismutase 2; Ho-1 - hemoxigenase 1.
