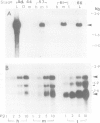
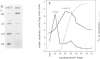
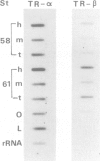
Abstract
The expression of genes encoding receptors for estrogen and thyroid hormones, as well as total c-erb-A related transcripts was determined in unfertilized eggs, all stages of embryonic and larval development and in adult tissues of Xenopus, by quantitative Northern and slot-blot hybridization. DNA and antisense RNA probes complementary to Xenopus c-myc, cytoskeletal actin and albumin mRNAs served as controls or developmental markers. Hybridization to full-length chicken c-erb-A cDNA at moderate stringency revealed a complex biphasic ontogenic pattern for several c-erb-A related mRNAs in all tissues and at all developmental stages, an increase of 4-fold in the accumulation of these transcripts occurring before metamorphosis (stages 30 to 40-42) and followed by a gradual build-up after mid-metamorphosis (stage 56). Using full-length or ligand-binding domain fragments of thyroid hormone (TR) and estrogen (ER) cDNAs under stringent hybridization conditions, transcripts of TR and ER were detected from stages 44 and 54 onwards, respectively. The alpha and beta forms of TR mRNAs exhibited different patterns of accumulation during development, the former transcript being present in substantially higher amounts at all developmental stages. The distinct patterns of accumulation of TR and ER mRNAs could be correlated with the differential pattern of early developmental acquisition of sensitivity of Xenopus larval tissues to thyroid hormone and estrogen.
Full text
PDF

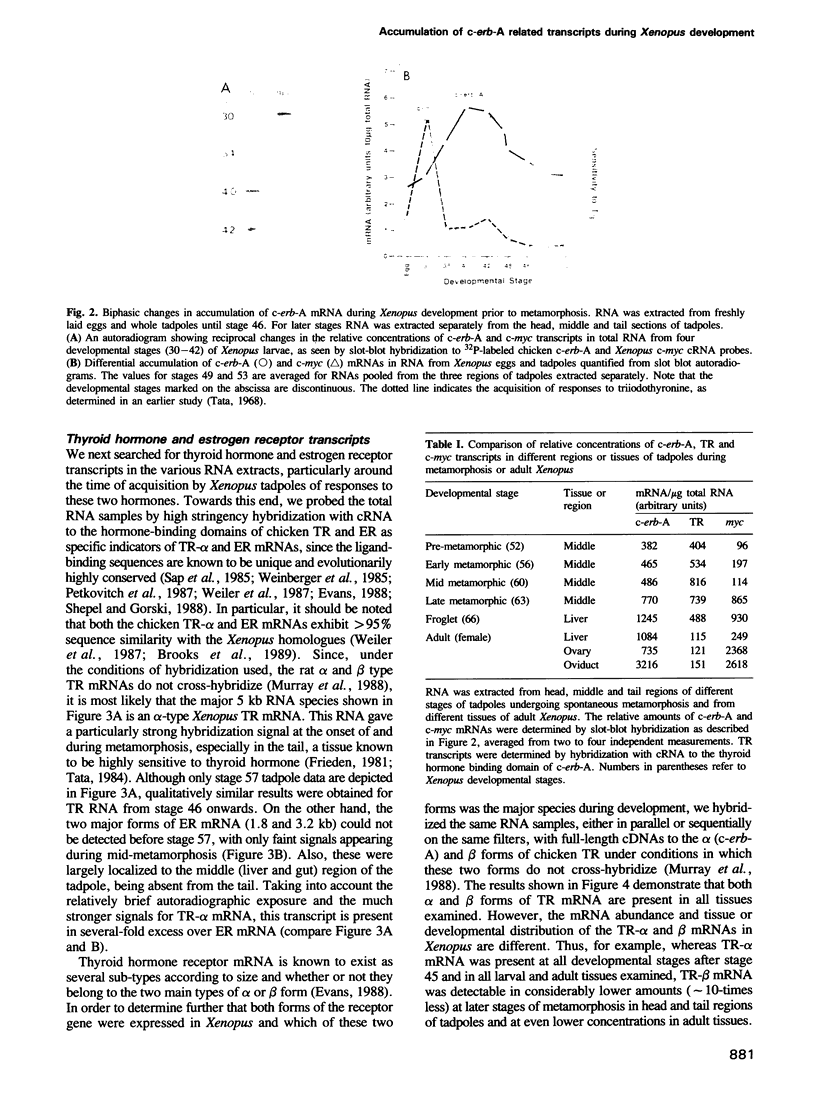



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks A. R., Sweeney G., Old R. W. Structure and functional expression of a cloned Xenopus thyroid hormone receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9395–9405. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. A superfamily of potentially oncogenic hormone receptors. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):615–617. doi: 10.1038/324615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Growth factors: mechanism of action and relation to oncogenes. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90296-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourdry J., Brulfert A., Gusse M., Schoevaert D., Taylor M. V., Mechali M. Localization of c-myc expression during oogenesis and embryonic development in Xenopus laevis. Development. 1988 Dec;104(4):631–641. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber S., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Thyroid hormone induces competence for oestrogen-dependent vitellogenin synthesis in developing Xenopus laevis liver. Nature. 1979 Mar 1;278(5699):65–67. doi: 10.1038/278065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara A., Kohara S., Amano M. Thyroid hormone directly induces hepatocyte competence for estrogen-dependent vitellogenin synthesis during the metamorphosis of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;132(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90206-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowland J. Induction of vitellogenin synthesis in Xenopus laevis tadpoles. Differentiation. 1978 Nov 15;12(1):47–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb00989.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Brent G. A., Larsen P. R., Chin W. W., Moore D. D. Inhibition of thyroid hormone action by a non-hormone binding c-erbA protein generated by alternative mRNA splicing. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):659–661. doi: 10.1038/337659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Knowland J. Oestrogen receptor levels and vitellogenin synthesis during development of Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1981 Aug 27;292(5826):853–855. doi: 10.1038/292853a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T. J., Garrett N. An amphibian cytoskeletal-type actin gene is expressed exclusively in muscle tissue. Development. 1987 Oct;101(2):393–402. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Zilz N. D., McCreary N. L., MacDonald M. J., Towle H. C. Isolation and characterization of rat cDNA clones for two distinct thyroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12770–12777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng W. C., Wolffe A. P., Tata J. R. Unequal activation by estrogen of individual Xenopus vitellogenin genes during development. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):238–247. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K. Expression of c-myc proto-oncogene during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Oncogene Res. 1987 Jul;1(2):179–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman A. J., Wolffe A. P., Champion J., Tata J. R. Regulation by estrogen receptor of vitellogenin gene transcription in Xenopus hepatocyte cultures. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1984 Dec;38(2-3):151–161. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(84)90113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J. J., Price M. P., Frieden E. Triiodothyronine increases translatable albumin messenger RNA in Rana catesbeiana tadpole liver. J Exp Zool. 1988 Jul;247(1):69–76. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402470110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepel L. A., Gorski J. Steroid hormone receptors and oncogenes. Biofactors. 1988 Jan;1(1):71–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipper J. K., Hamilton T. H. Xenopus liver: ontogeny of estrogen responsiveness. Science. 1979 Nov 9;206(4419):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.493974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Peptide growth factors are multifunctional. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):217–219. doi: 10.1038/332217a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strähle U., Boshart M., Klock G., Stewart F., Schütz G. Glucocorticoid- and progesterone-specific effects are determined by differential expression of the respective hormone receptors. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):629–632. doi: 10.1038/339629a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tata J. R. Early metamorphic competence of Xenopus larvae. Dev Biol. 1968 Nov;18(5):415–440. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor M. V., Gusse M., Evan G. I., Dathan N., Mechali M. Xenopus myc proto-oncogene during development: expression as a stable maternal mRNA uncoupled from cell division. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3563–3570. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Giguere V., Glass C. K., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid and thyroid hormone induce gene expression through a common responsive element. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):262–265. doi: 10.1038/336262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler I. J., Lew D., Shapiro D. J. The Xenopus laevis estrogen receptor: sequence homology with human and avian receptors and identification of multiple estrogen receptor messenger ribonucleic acids. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 May;1(5):355–362. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-5-355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Glover J. F., Martin S. C., Tenniswood M. P., Williams J. L., Tata J. R. Deinduction of transcription of Xenopus 74-kDa albumin genes and destabilization of mRNA by estrogen in vivo and in hepatocyte cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):489–496. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08678.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Molecular analysis of signal transduction by growth factors. Biochemistry. 1988 May 3;27(9):3113–3119. doi: 10.1021/bi00409a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]