Figure 3.
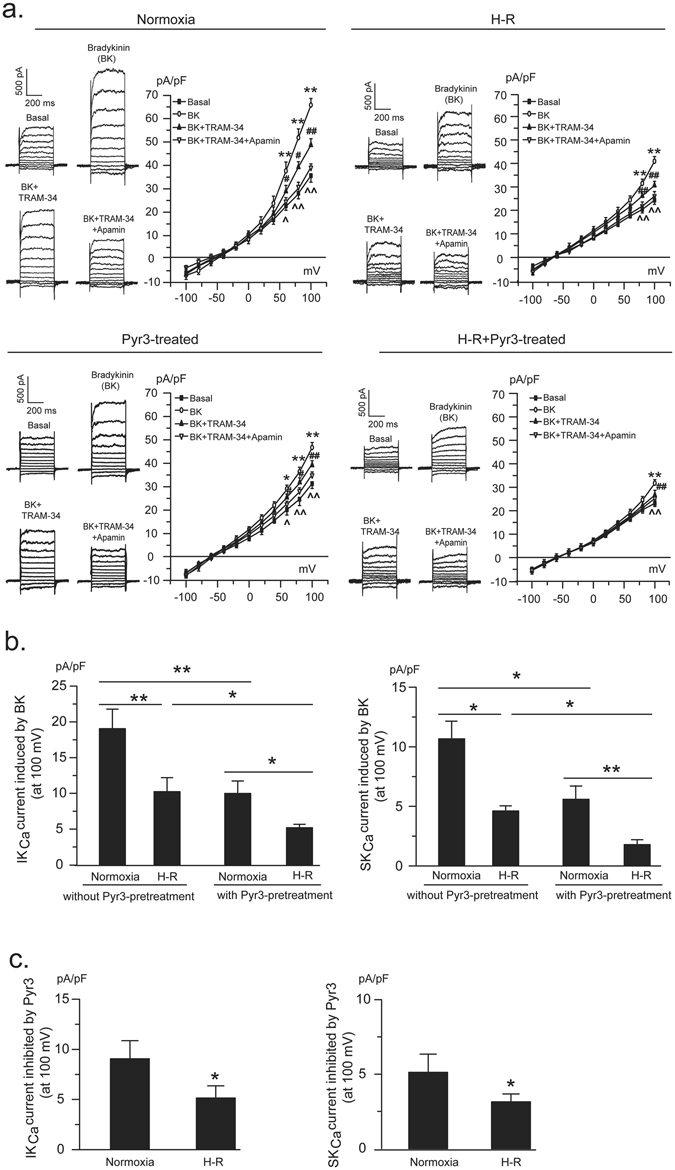
Inhibition of TRPC3 channels contributes to H-R-induced suppression of IKCa and SKCa channel activity in PCAECs. Representative traces and current-voltage relationship of whole-cell K+ current in PCAECs from different treatment groups before and after bradykinin (BK) stimulation with further application of the IKCa channel blocker TRAM-34 and the SKCa blocker apamin (a). In H-R group, cells were exposed to 60-min hypoxia and 30-min reoxygenation before patch-clamp recording. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, BK vs. basal; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, BK + TRAM-34 vs. BK; ^p < 0.05, ^^p < 0.01, BK + TRAM-34 + Apamin vs. BK + TRAM-34. Pre-treatment of PCAECs with the selective TRPC3 channel blocker Pyr3 significantly inhibited BK-induced IKCa and SKCa channel currents under both normoxic and H-R conditions (b). Pyr3 exhibited less inhibition on both components of IKCa and SKCa induced by BK when compared with the cells without H-R exposure (c). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA and Scheffe post-hoc test (a and b) and unpaired t test (c). n = 5 in each group. N indicates the number of independent experiments, each obtained from cell isolates of different hearts.
