Figure 3.
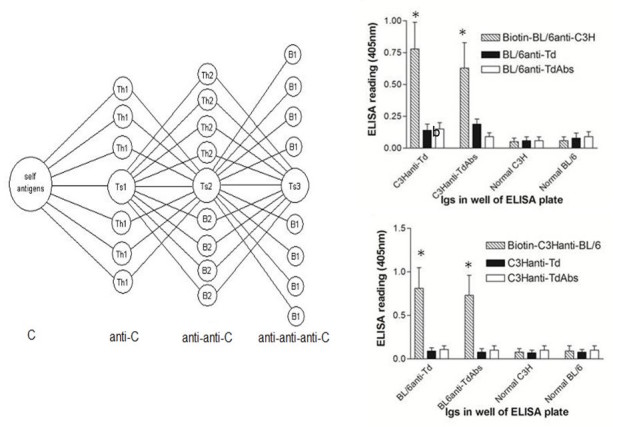
In the symmetrical immune network theory (left hand panel), self antigens of a vertebrate C stimulate Th1 and Ts1 lymphocytes (anti-C), which are co-selected with Th2, Ts2 and B2 lymphocytes (anti-anti-C), which in turn co-select Ts3 and B1 lymphocytes (anti-anti-anti-C). B2 cells are IgG-secreting B lymphocytes, and B1 cells are IgM‑secreting B lymphocytes. Anti-foreign and anti‑anti-self antibodies are produced in BL/6 and C3H mice immunized with tetanus toxoid (Td)-right hand panels. All IgGs were coated on ELISA plates at 50ng/well. All developing sera were used at 1:400 concentration, with streptavidin HRP used at 1:2000. In the upper panel, biotinylated BL/6 anti-C3H IgG binds to C3H anti-Td IgG and to C3H anti-Td IgG absorbed with Td. The lower panel shows the converse, with biotinylated C3H anti-BL/6 IgG binding to BL/6 anti-Td IgG. All data are from a total of 10 mice/group; *P<.05, MANOVA.
