Figure 1.
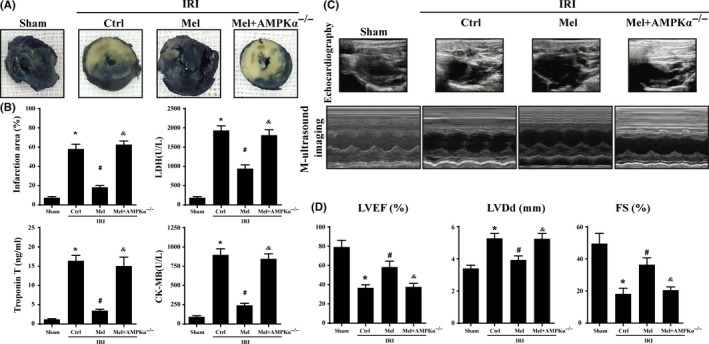
Melatonin reduced infarct size and preserved cardiac function following ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo which was performed by 30 min of ischemia followed by 2‐h reperfusion (n=6/group). (A). Representative pictures of heart sections with TTC and Evans Blue staining. (B). Bar graph indicates the infarct size expressed as a percentage of the total left ventricular area. The lactate dehydrogenase release, troponin T contents, and CK‐MB values were assessed via ELISA. (C). Representative M‐mode echocardiograms was performed after 2‐h reperfusion with the parasternal long‐axis views in each group. (D). Quantitative analysis of cardiac function by echocardiography. *P<.05 vs sham group; #P<.05 vs Ctrl‐IRI group, &P<.05 vs Mel‐IRI group
