Figure 2.
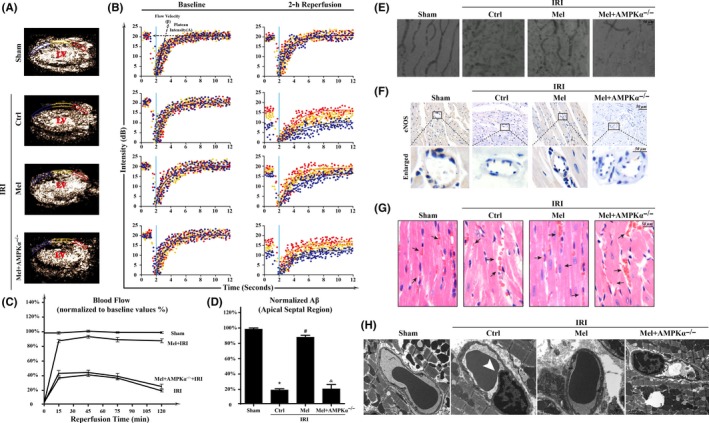
Melatonin protected acute microcirculation malfunction during ischemia/reperfusion injury(IRI) via AMPKα. (A‐B). Representative case of a myocardial contrast echocardiography myocardial contrast echocardiography parasternal long‐axis image, which was divided into three regions: apical septum (blue), mid‐septum (yellow), and basal septum (red). Left ventricular: Left ventricle. A: plateau intensity, β: flow velocity. (C). Myocardial blood flow (A×β) profiles in the apical region for different groups at 15, 45, 75, and 120 min after reperfusion. (D). Apical myocardial blood flow 120 min after reperfusion. n=6 per group. (E). Microvascular image detection by ink staining. (F). Immunohistochemistry of endothelial nitric oxide synthaseS expression. (G). HE staining for red blood cell morphology in different groups. (H). Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to observe the structural changes of microvessel in response to IRI, including microvascular wall destruction and luminal stenosis (white arrow) of CMEC. *P<.05 vs sham group, #P<.05 vs Ctrl‐IRI group, &P<.05 vs Mel‐IRI group
