Figure 4.
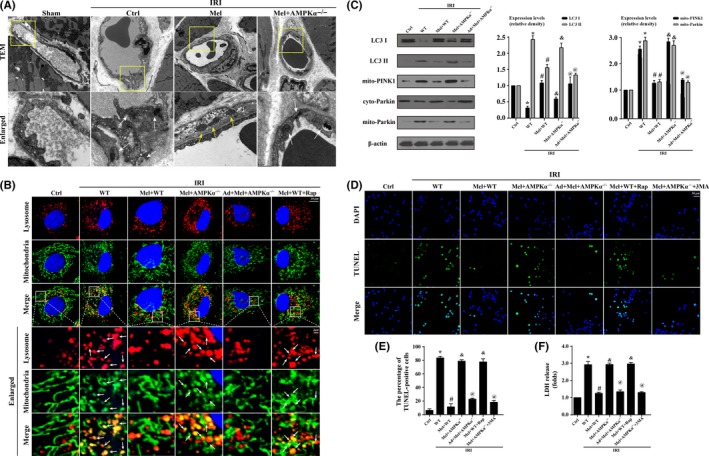
Ischemia/reperfusion injury induced(IRI) cardiac microcirculation endothelial cells(CMEC) death via excessive mitophagy in vitro. Wild‐type mice‐ and AMPKα−/− mice‐derived CMEC treated with melatonin were named Mel+WT and Mel+AMPKα−/− group, respectively. Furthermore, AMPKα gain‐of‐function experiments was performed in CMECs from AMPKα−/− using adenovirus vector following melatonin treatment, named Ad+Mel+AMPKα−/− group. Meanwhile, rapamycin (Rap), an activator of mitophagy, was used in Mel+WT as the positive control group. The IRI in vitro was mimicked by 30 min of hypoxia with serum starvation and 2 h of reoxygeneration. (A). Transmission electron microscope was performed to observe mitophagy in vivo. IRI induced more mitochondria were contained by lysosome, and these changes were reversed by melatonin. Yellow arrow suggested the normal mitochondria. White arrow indicated the digested mitochondria or fragmented mitochondria in lysosome. (B). The co‐location of lysosome and mitochondria. More fragmented mitochondria were consumed by lysosomes in response to IRI, which was reversed by melatonin. Rap reduced more numbers of mitochondria contained in lysosome. (C). The change of proteins related to mitophagy. IRI increased the ratio of LC3 II/LC3 I via PINK1/Parkin pathway activation. (D‐E). TUNEL staining demonstrated that mitophagy evoked CMEC death. (F). The lactate dehydrogenase release assay to detect cellular damage. 3‐MA, an inhibitor of mitophagy. *P<.05 vs Ctrl group, #P<.05 vs IRI‐WT group, &P<.05 vs IRI‐Mel+WT group, @P<.05 vs IRI‐Mel+ AMPKα−/− group
