Figure 1.
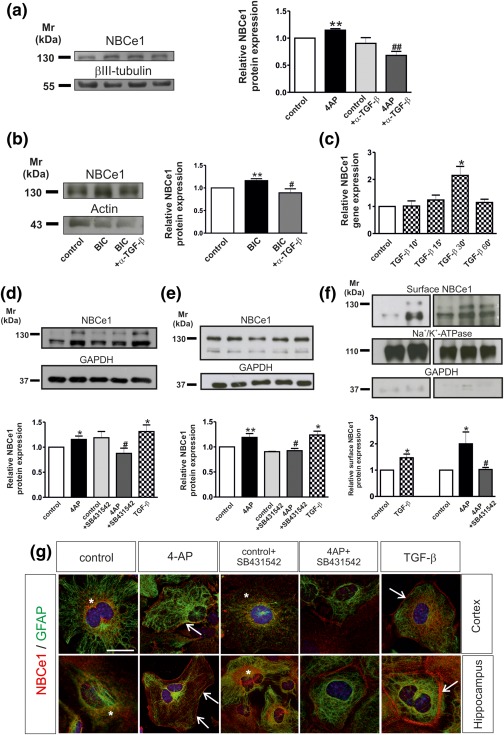
(a, b) Neutralization of endogenous TGF‐βs abolish 4‐AP‐ and bicuculline‐dependent NBCe1 upregulation in acute hippocampal slices. Immunoblotting for NBCe1 in control slices and following treatment with either 100 µM 4AP (a) or 20 µM bicuculline/0 Mg2+ (BIC) in the presence or absence of 20 µg/mL anti‐TGF‐β1,2,3 (α‐TGF‐β). Protein of 50 µg was loaded per lane, n = 3. (c) Time dependency of NBCe1 mRNA regulation in controls and following treatment with TGF‐β (2 ng/mL). Quantitative RT‐PCR analysis of cDNA from primary cortical astrocytes (*p < .05 for significant upregulation compared to controls, using the Student's t‐test, n = 3). (d, e) NBCe1 protein in cortical (d), and hippocampal (e) astrocytes following application of 4AP, 4AP in combination with the inhibitor of TGF‐β receptor II (10 µM, SB431642), or with 2 ng/mL recombinant TGF‐β. The blots are representative of six different experiments. Protein of 10 µg and 15 µg were loaded per lane for cortical and hippocampal astrocytes, respectively. (f) Immunoblot analysis of biotinylated cell surface proteins from cortical astrocytes for NBCe1. The blots are representative for three different experiments. Protein of 80 µg was loaded per lane. *p < .05, **p < .01 for significant increase, after densitometric analysis of the signal ratio NBCe1: βIII‐tubulin, NBCe1: actin, NBCe1: GAPDH, or NBCe1:Na+/K+‐ATPase and Student's t‐test, compared to the controls. # p < .05 and ## p < .01 for significant decrease compared to 4AP treatment using one‐way ANOVA and Bonferroni post hoc test. (g) Double immunofluorescence for NBCe1 and GFAP in primary cortical and hippocampal astrocytes. Nuclei are stained with DAPI. Arrows point to membrane NBCe1 and * indicates intracellular NBCe1 distribution. Scale bar: 10 µm
