Figure 1.
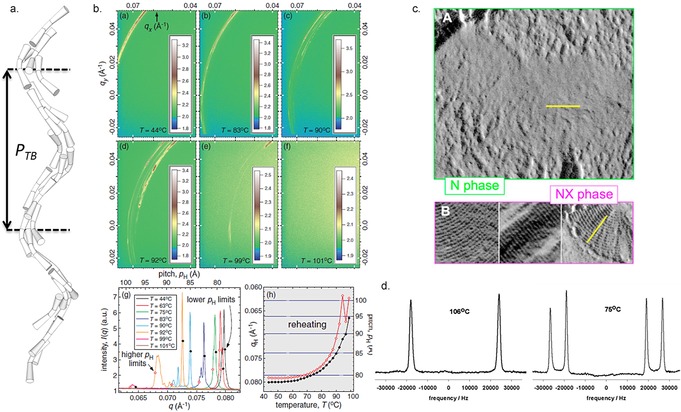
The twist–bend nematic phase: a) Cartoon depiction of a bent, U‐shaped dimers with a bend angle of ≈110° forming a NTB phase whose pitch (P TB) is about 3.5 times the dimer length. b) Resonant small‐angle X‐ray scattering at the carbon K‐edge (E=283.5 eV) of the dimer CB9CB at various temperatures in the NTB and classical nematic mesophases on a silicon nitride surface, reprinted from reference 9, copyright 2016 by the American Physical Society. c) Comparison of the freeze–fracture TEM image of CB7CB in the nematic phase quenched at 105 °C (A) and the NTB phase quenched at 95 °C (B, labelled as NX)—in both mesophases the scale bar corresponds to 100 nm (reproduced from reference 7, used with permission of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, copyright 2013).7 d) 1H NMR spectra of [D2]8CB dissolved in CB7CB and recorded in the nematic (106 °C, 46.0 MHz) and twist–bend nematic (75 °C, 61.4 MHz), adapted with permission from reference 15, copyright American Chemical Society 2012.15
