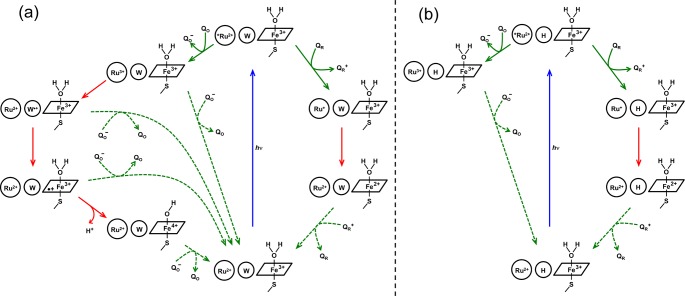
Figure 6.
Photochemical ET reaction scheme in RuC97(CYP102A1) and RuC77(CYP119). Blue arrows indicate excitation processes, solid green arrows indicate bimolecular quenching reactions, dashed green arrows indicate bimolecular charge-recombination processes with quencher redox products, and red arrows indicate intraprotein ET reactions. With an intervening W residue (a, CYP102A, W96; CYP119 H76W), oxidative quenching of *Ru2+ by QO (left path) leads to heme oxidation via an intermediate Trp radical; reductive quenching by QR (right path) leads to heme reduction in a single-step tunneling reaction. With an intervening H residue (b, CYP102A, W96H; CYP119 H76), oxidative quenching of *Ru2+ by QO produces Ru3+ but not heme oxidation, whereas reductive quenching again leads to single-step electron transfer from Ru+ to the heme.