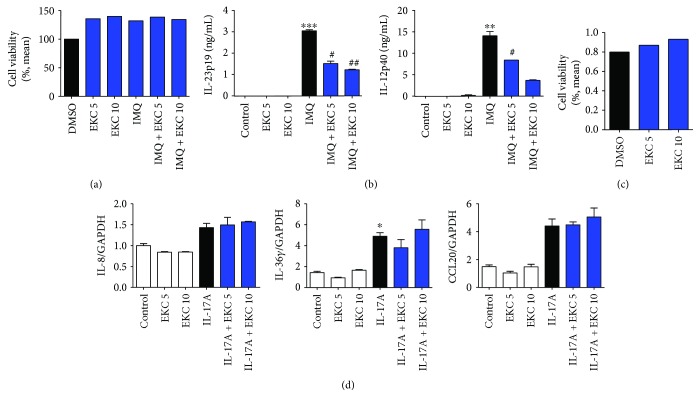
Figure 7.
Reduced production of IL-12 and IL-23 in IMQ-stimulated dendritic cells by EKC. (a) JAWSII cells were plated at 2 × 105 cells/well in a 96-well plate. EKC (5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL) dissolved in DMSO (final concentration of 0.05%) was added to the cells, which were then cultured for 24 h with or without IMQ (1 μg/mL). Cytotoxicity was analyzed by MTT assay. (b) JAWSII cells (1 × 106) were plated in a 24-well multiplate, cultivated with EKC (5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL), and treated with or without IMQ (1 μg/mL). After 18 h, total RNA was isolated from each sample and reverse-transcribed cDNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Values represent the mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with control (0.05% DMSO); #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01 compared with the IMQ group. (c) HaCaT cells were plated at 2 × 105 cells/well in a 96-well plate. EKC (5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL) dissolved in DMSO (final concentration of 0.05%) was added, and the cells were cultured for 24 h. Cytotoxicity was analyzed by MTT assay. (d) HaCaT cells (1 × 106) were plated in a 24-well multiplate, cultivated with EKC (5 μg/mL and 10 μg/mL), and treated with or without human IL-17A (100 ng/mL). After 18 h, total RNA was isolated from each sample and reverse-transcribed cDNA was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR). Values represent the mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05 compared with control (0.05% DMSO).