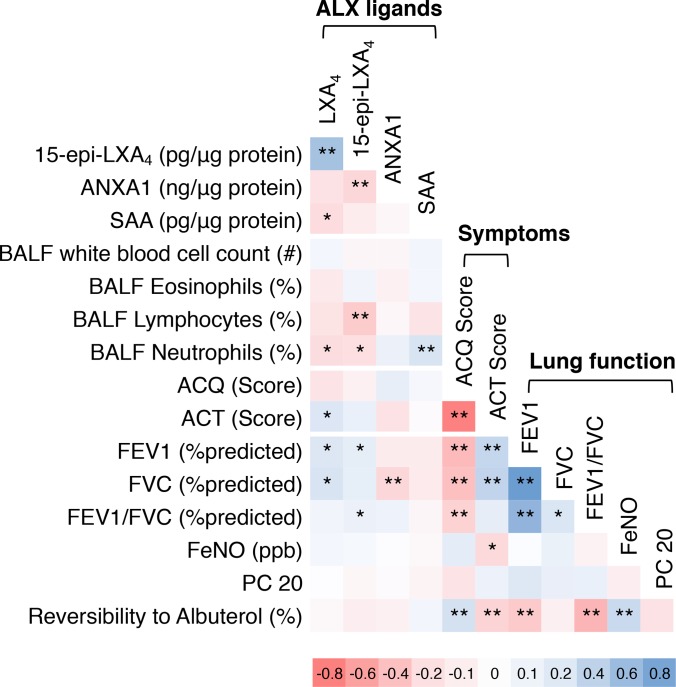
Figure 2. Relationship between ALX ligands, lung inflammation, asthma symptoms, and lung function in asthma.
The relationships between BALF ALX ligand levels, BAL leukocytes, asthma symptom score, and measures of lung function, were determined by Pearson correlation matrix (see Methods) for n = 51 NSA and n = 69 SA subjects. Positive correlations are noted in blue and negative correlations in red. The color intensity is proportional to Pearson’s correlation coefficient, with deeper colors denoting stronger associations. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 by Pearson correlation analysis. BALF, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid; ALX, airway lipoxin A4 receptor; NSA, nonsevere asthma; SA, severe asthma; LXA4, lipoxin A4; 15-epi-LXA4, 15-epimer lipoxin A4; ANXA1, annexin A1; SAA, serum amyloid A; ACQ, Asthma Control Questionnaire; ACT, Asthma Control Test; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC, forced vital capacity; FeNO, fractional exhaled nitric oxide; PC 20, provocation challenge causing a 20% fall in FEV1.