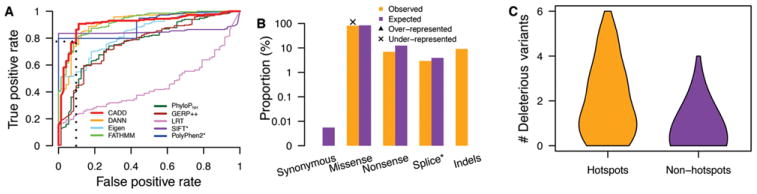
Figure 3.
Prediction of potentially pathogenic mutations in the five human RECQ helicase genes. A: Sensitivity analysis of ability of nine prediction metrics to distinguish pathogenic variants in RECQMutdb from benign variants as indicated by ROC analysis. The values of AUC for the nine metrics are 0.91 (CADD), 0.91 (DANN), 0.84 (Eigen), 0.92 (FATHMM), 0.77 (PhyloPNH), 0.76 (GERP++), 0.50 (LRT), 0.85 (SIFT), and 0.90 (PolyPhen2), respectively. All metrics, except CADD, annotate only point mutations/SNVs, with SIFT and PolyPhen2 further restricted to missense variants. B: The proportion of potentially pathogenic variants in ESP, 1KGP, and ExAC data (CADD ≥ 24) as a function of functional consequences compared with expectation by imputing all possible single base changes by Fisher’s exact test. Only missense-generating variants were significantly under-represented (P < 0.05) compared with expectation (marked by “x”). C: The distribution of the number of potentially pathogenic variants across all five human RECQ helicase genes residing in either 10-bp mutational hotspots or in non-hotspots.