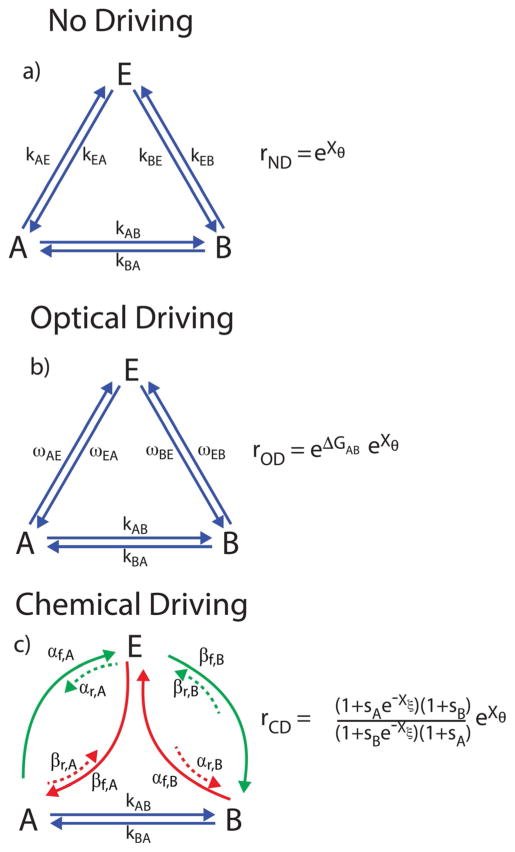
Figure 12.
Triangle reaction with an external load Xθ and: a) no external driving (ND); b) optical driving (OD); and c) chemical driving (CD). The ratio, r, is the probability of a counterclockwise cycle divided by the probability of a clockwise cycle, and is calculated as the ratio of the product of the counterclockwise rates divided by the product of the clockwise rates. In very bright light, the optical transition coefficients obey the simple relation ωAE ≈ ωEA and ωBE ≈ ωEB. In contrast, the ratio of each forward and reverse rate constant for each pair of processes that are microscopic reverses of one another must be proportional to the exponential of the free-energy difference of the states they connect [see Eq. (2)].