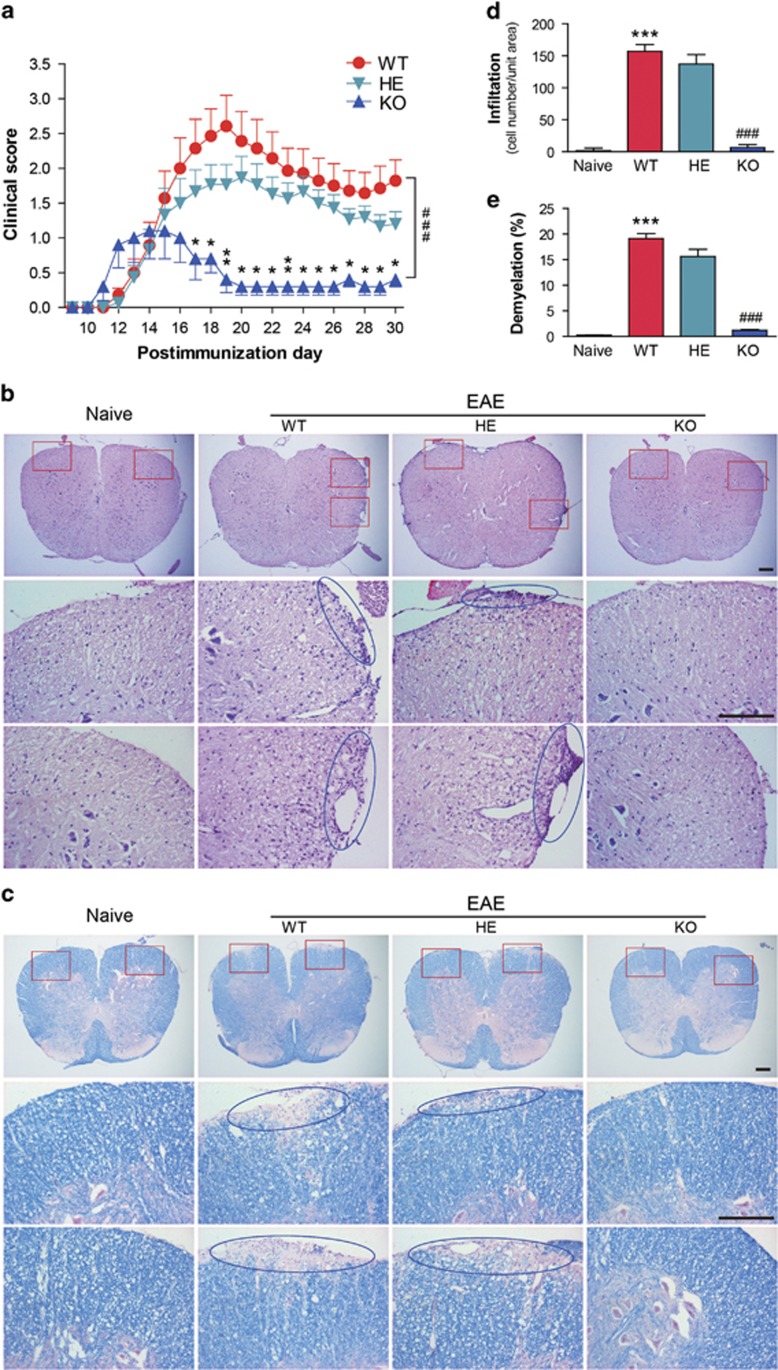
Figure 2.
Gαq-KO suppresses EAE pathogenesis. (a) Clinical scores of EAE in WT (n=14), heterozygous (n=15) and Gαq-KO (n=5) mice. The data are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. ###P<0.001 versus WT group throughout the disease course (two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)), *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 versus WT on any given day (Mann–Whitney U-test). (b) Hematoxylin and eosin and (c) Luxol Fast Blue staining of the paraffin sections of the spinal cords isolated from naive and EAE-induced WT, heterozygous, and Gαq-KO mice on day 17 PI, and boxed areas in the top column are enlarged and presented at the bottom; the circular areas show infiltration or demyelination. Scale bars, 200 μm. (d and e) Quantization of CNS infiltrates; the percentages of demyelination presented in (b) and (c) were quantified by Image-Pro. Five mice from each group were killed, and 20 sections from each mouse were analyzed. The data are expressed as the mean±s.e.m. ***P<0.001 versus naive group, ###P<0.001 versus WT-EAE.