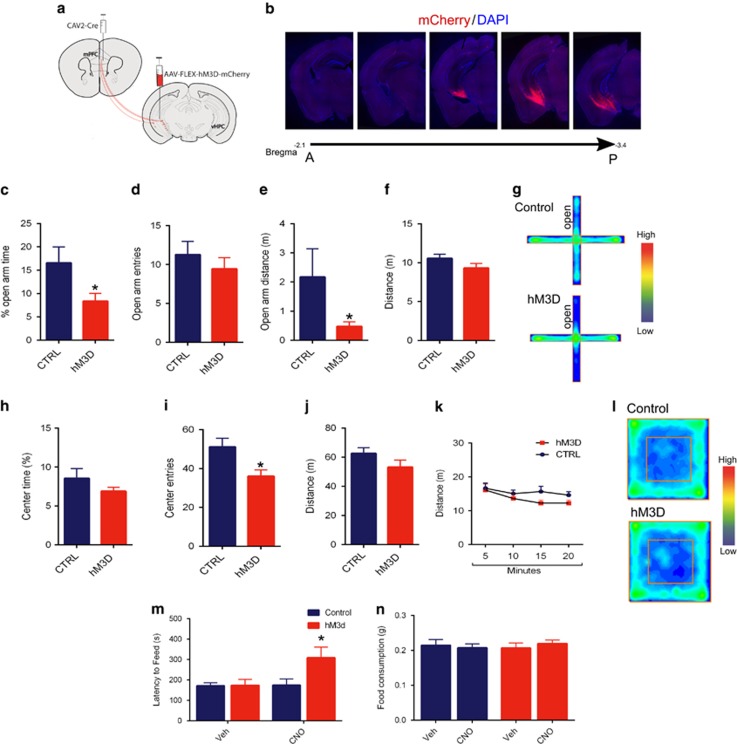
Figure 4.
hM3D-mediated activation of mPFC-projecting vHPC cells increases anxiety. (a) mPFC-projecting vHPC cells were targeted by injecting the retrogradely propagating CAV2-Cre virus into the mPFC and injecting AAV8FLEXhM3DmCherry into the vHPC. (b) Representative images from AAV8FLEXhM3DmCherry mice showed hM3D-mCherry expression in mPFC-projecting vHPC cells along the anterior–posterior axis. (c–e) hM3D mice displayed a decreased % open arm time (*p=0.002) and open arm distance (*p<0.05) without change in the number of open arm entries. (f) CTRL and hM3D mice showed similar levels of locomotor activity measured as a total distance traveled in the EPM. (g) Heat-map plots show the averaged cumulative time spent in different parts of the EPM. red=more time, blue=less time. (h and i) hM3D mice displayed a decreased center entries (*p=0.01) after CNO injection, without changes in % center time. (j) CTRL and hM3D mice showed similar levels of locomotor activity measured as a total distance traveled in the OF. (k) Examination of locomotor activity in 5 min intervals revealed no significant differences between hM3D and CTRL mice. (l) Heat-map plots show the averaged cumulative time spent in different parts of the OF. red=more time, blue=less time. (m) CNO increased the latency to feed in hM3D mice but not in CTRL mice in the NSF test (RM two-way ANOVA shows a significant effect of the treatment F(1, 16)=5.371 *p=0.034, followed by Bonferroni post-test p=0.004). (n) No alteration the food consumption was observed among the groups after the NFST. n=7 for CTRL and 11 for hM3D mice.