Figure 1. Structure of the NMDA receptor.
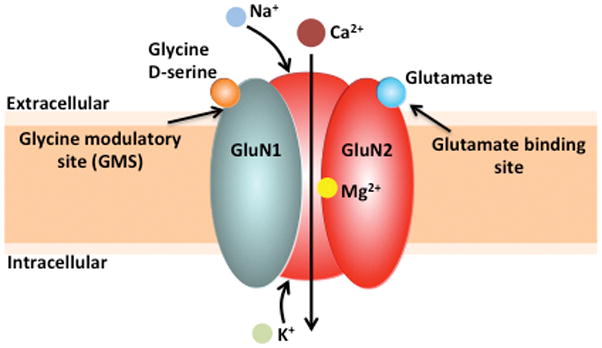
The conventional NMDAR ion channel is heterotetrameric, consisting of two GluN1 and two GluN2 subunits. These receptors act as molecular coincidence detectors, as in addition to the binding of its agonist glutamate to the GluN2 subunit, activation of the NMDAR requires 1) post-synaptic depolarization, which relieves the Mg2+ blockade of the channel and 2) either glycine or D-serine must be bound at the glycine modulatory site (GMS) on the GluN1 subunit. Upon NMDAR channel opening, calcium (Ca2+) and sodium (Na+) enter the neuron, while potassium (K+) exits the neuron.
