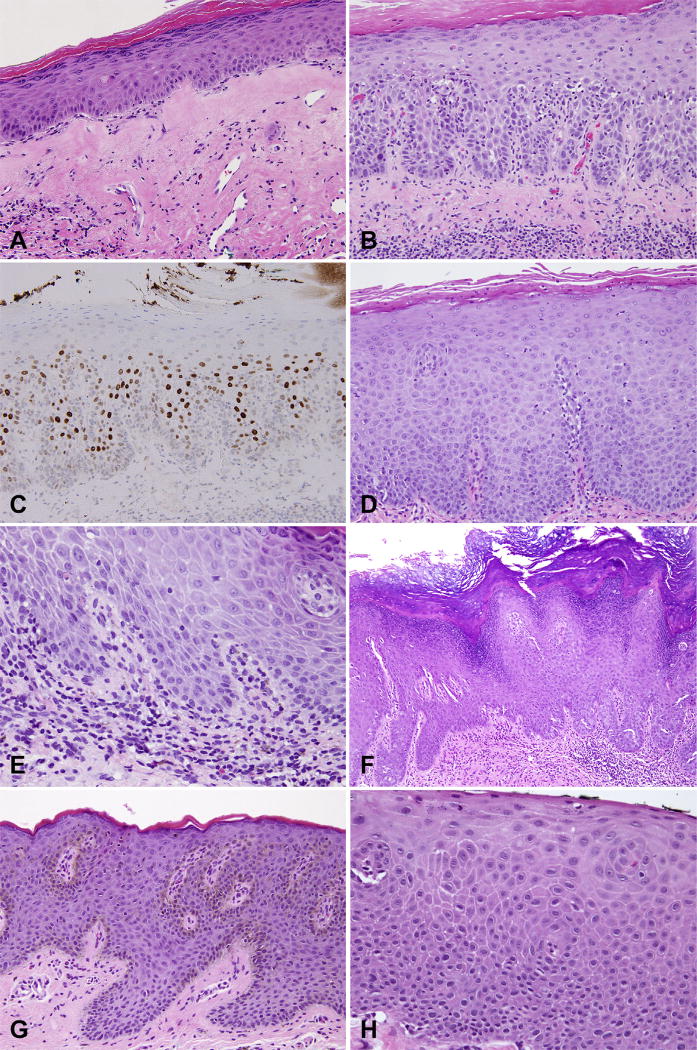
Fig. 5.
Differential diagnosis for vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN). (A) Lichen sclerosus; (B) hypertrophic lichen sclerosus with (C) increased p53 staining; (D) squamous hyperplasia due to candida; (E) spongiotic dermatitis with rare eosinophils; (F) pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia due to extramammary Paget’s disease; (G) squamous hyperplasia due to melanoma in situ; (H) basaloid variant of dVIN mimicking uVIN.