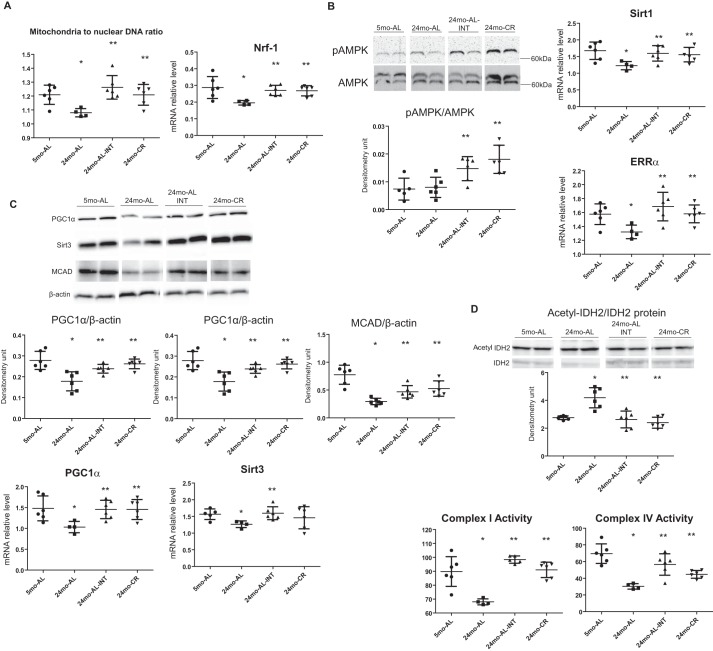
Figure 2.
INT-767 treatment increases mitochondrial biogenesis and function. A, INT-767 increases the mitochondrial to nuclear DNA ratio and mRNA level of NRF1 in aging kidneys. B, INT-767 treatment increases the activated AMPK level and prevents the age-related decreases in SIRT1 mRNA and nuclear hormone receptor ERR-α mRNA. C, INT-767 prevents the age-related decrease in PGC-1α mRNA and protein; mitochondrial SIRT3 mRNA and protein; and its target, MCAD protein. D, INT-767 reverses the age-related increase in the acetylated form of mitochondrial isocitrate dehydrogenase as shown in the Western blot. 2-month INT-767 treatment also reverses the decreased mitochondrial complex I and complex IV activity in aged kidneys. Error bars represent S.D. n = 6 mice. *, p < 0.05 versus 5-month-old ad libitum fed (5mo-AL); **, p < 0.05 versus 24-month-old ad libitum fed (24mo-AL). INT, INT-767-treated; CR, calorie-restricted.