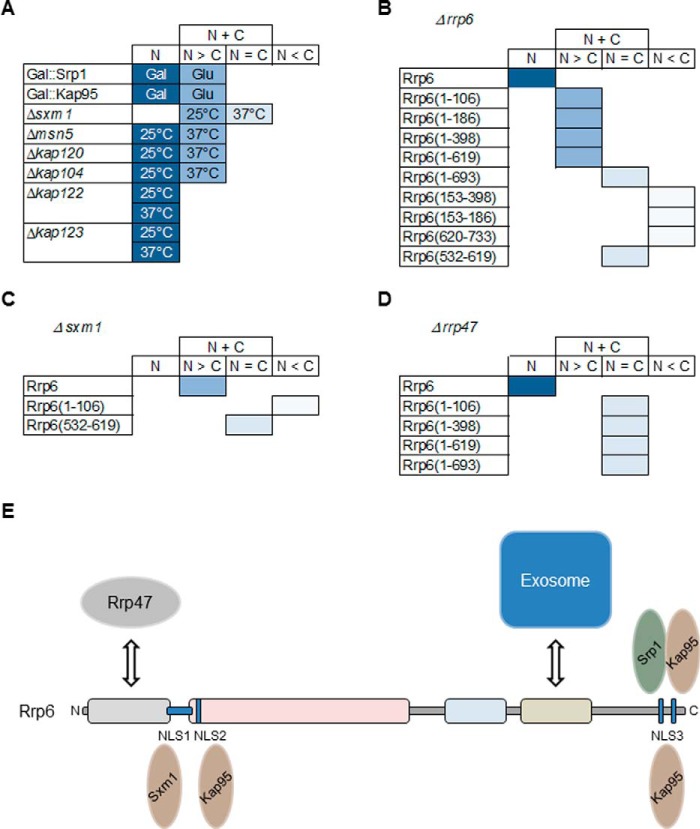
Figure 10.
A, score chart to summarize the effects of karyopherin depletions (Srp1 and Kap95; galactose (Gal) or glucose (Glu)) or deletions (Sxm1, Msn5, Kap104, Nmd5, Kap120, Kap114, Kap122, and Kap123; 25 or 37 °C) on Rrp6 localization. B, localization of Rrp6 deletion mutants in the Δrrp6 strain. C, localization of Rrp6 deletion mutants in the Δsxm1 strain. D, localization of Rrp6 deletion mutants in the Δrrp47 strain. N, nuclear localization; N > C, mainly nuclear but also present in cytoplasm; N = C, protein visualized both in nucleus and cytoplasm; N < C, protein mainly present in cytoplasm. E, model of the alternative and overlapping pathways for the nuclear import of Rrp6. Rrp6 transport to the nucleus can be facilitated by the α/β dimer Srp1–Kap95 recognizing the canonical NLS3 at the C-terminal portion of Rrp6 or by the β-importins Kap95 and Sxm1 recognizing one of its nuclear localization signals. Alternatively, Rrp6 could be transported in a subcomplex with the exosome complex or other exosome-interacting proteins.