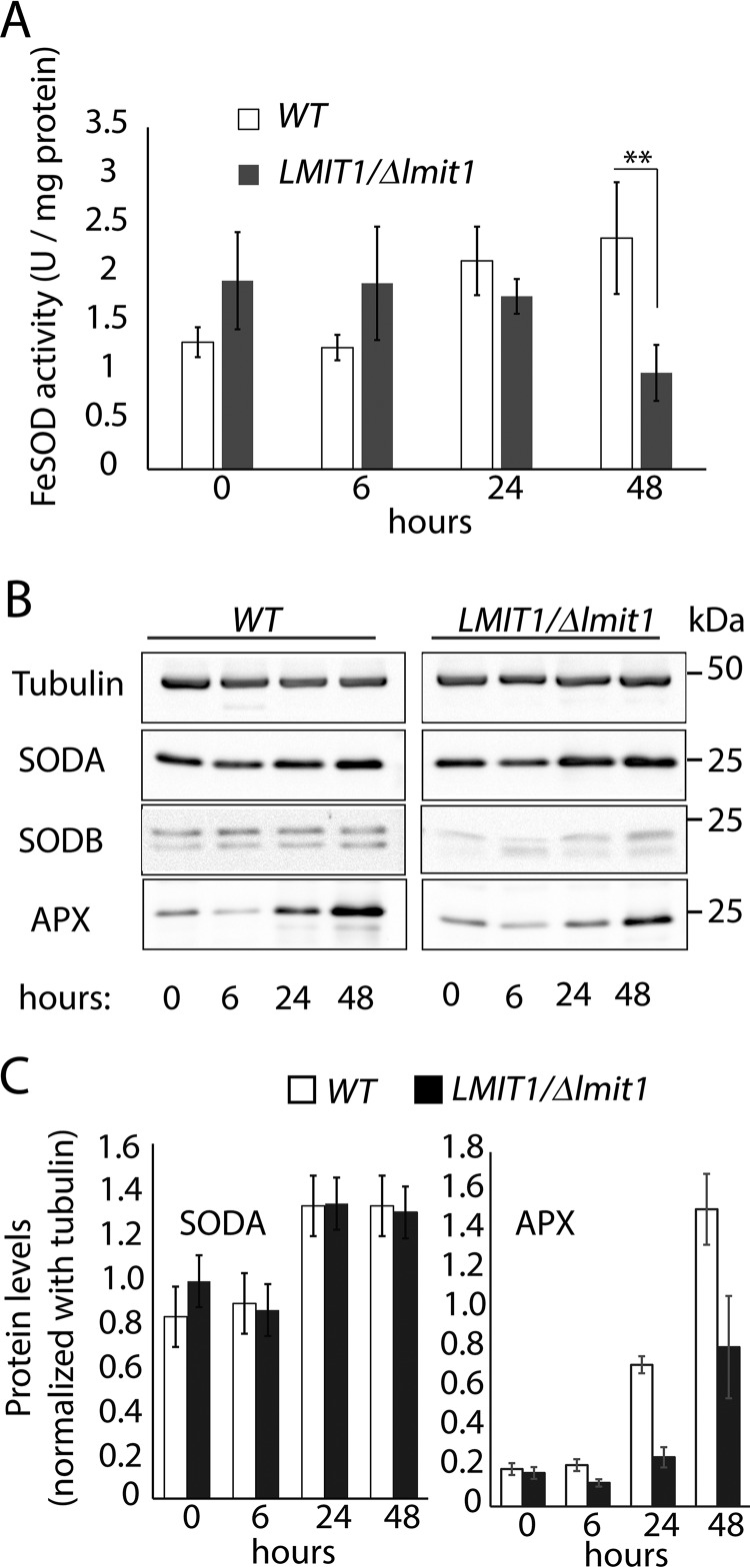
Figure 2.
LMIT1/Δlmit1 promastigotes undergoing axenic differentiation show similar SODA protein levels but reduced mitochondrial SOD activity. A, log phase (∼2 × 107/ml) wild-type (WT) and single knock-out (LMIT1/Δlmit1) promastigotes were induced to differentiate into axenic amastigotes by shifting to pH 4.5/32 °C culture conditions and incubated for 48 h. Mitochondrion-enriched pellet fractions prepared by digitonin (1 mg/ml) treatment of parasites were collected at the indicated time points and assayed for SOD activity. The data represent the mean ± S.D. of triplicate determinations and are representative of four independent experiments (Student's t test compared with WT: **, p = 0.008). B, mitochondrial extracts used for the SOD assay were resolved by 12% SDS-PAGE (10 μg protein/lane), and Western blottings were probed with specific antibodies against SODA, SODB, and APX. Anti-tubulin antibodies were used was used as loading controls. C, SODA protein levels relative to the tubulin in mitochondrial extracts, estimated by quantification of the respective band intensities on Western blottings.